|
|
|
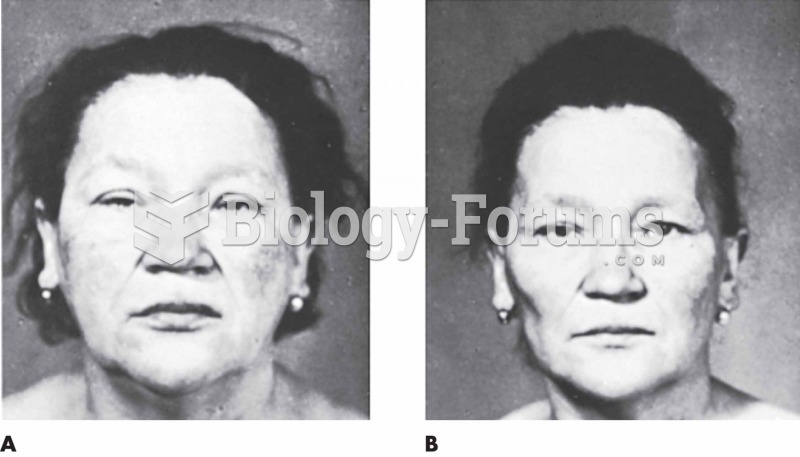
Chronic necrotizing aspergillosis has a slowly progressive process that, unlike invasive aspergillosis, does not spread to other organ systems or the blood vessels. It most often affects middle-aged and elderly individuals, spreading to surrounding tissue in the lungs. The disease often does not respond to conventionally successful treatments, and requires individualized therapies in order to keep it from becoming life-threatening.
The first documented use of surgical anesthesia in the United States was in Connecticut in 1844.
Acute bronchitis is an inflammation of the breathing tubes (bronchi), which causes increased mucus production and other changes. It is usually caused by bacteria or viruses, can be serious in people who have pulmonary or cardiac diseases, and can lead to pneumonia.
Essential fatty acids have been shown to be effective against ulcers, asthma, dental cavities, and skin disorders such as acne.
Thyroid conditions may make getting pregnant impossible.
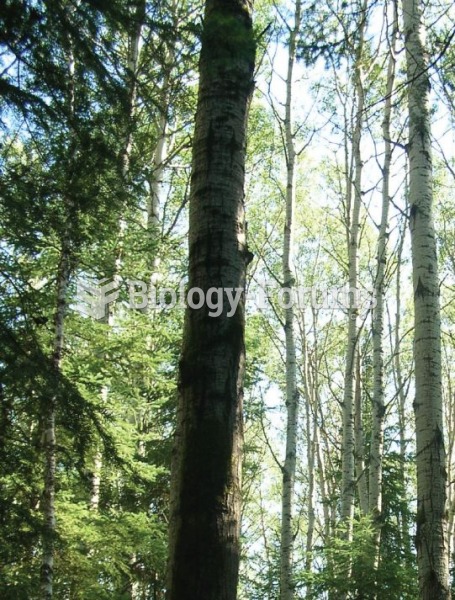 Changes in boreal forest composition along a chronosequence in Quebec. Dates refer to the year of th
Changes in boreal forest composition along a chronosequence in Quebec. Dates refer to the year of th
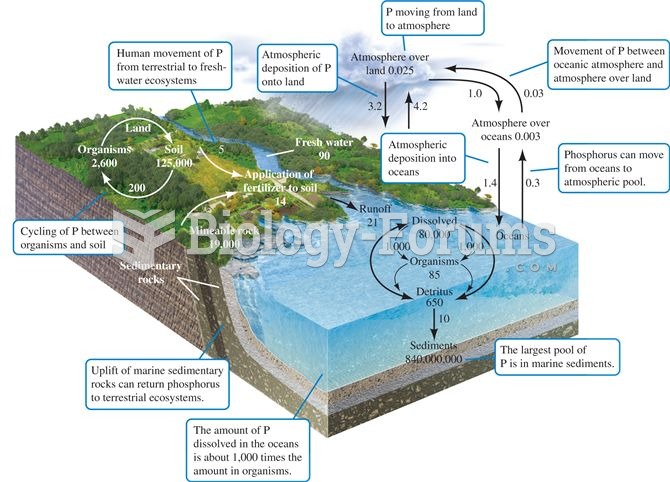 The phosphorus cycle. Numbers are 1012 g P or fluxes as 1012 g P per year (data from Schlesinger 199
The phosphorus cycle. Numbers are 1012 g P or fluxes as 1012 g P per year (data from Schlesinger 199