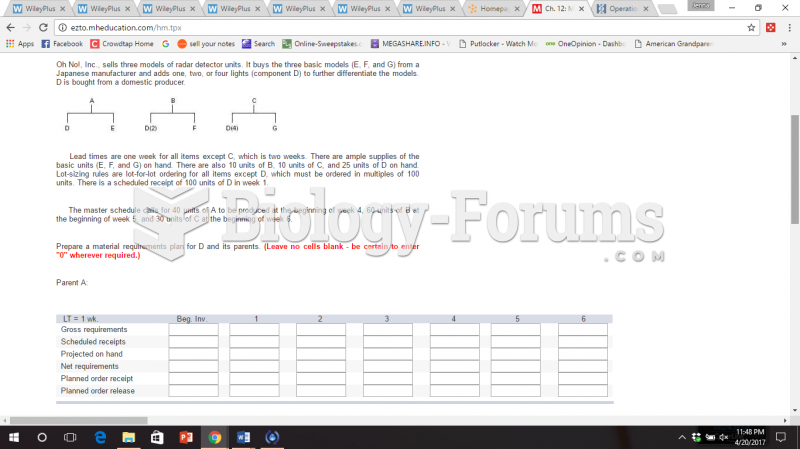
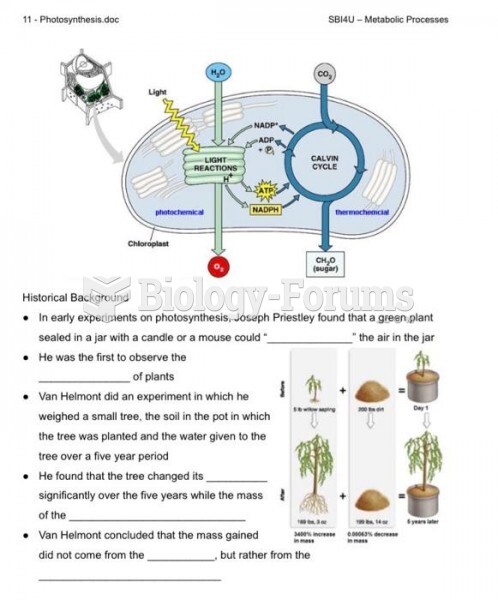
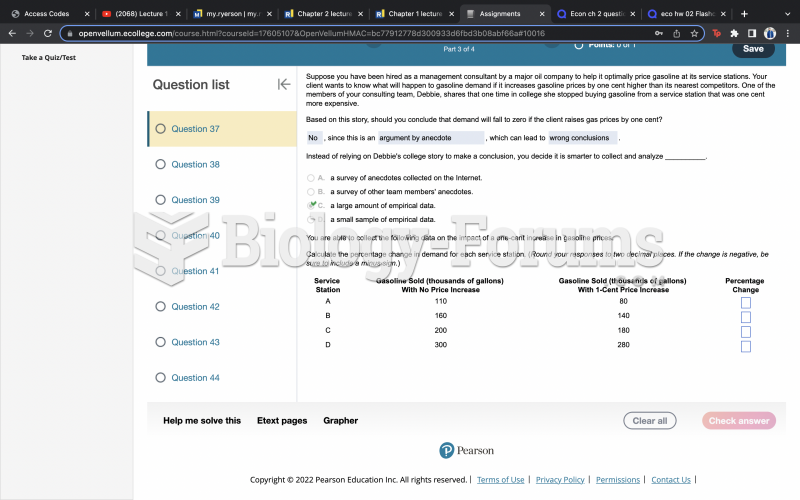
Answer to Question 1
A bite block is an appliance that is used to stabilize the mandible, which allows the therapist to evaluate or exercise other articulars. Bite blocks are available in many shapes and sizes. They are also composed of different materials. Some bite blocks are made of acrylic blocks that are around 1 cm square. Other softer and more pliable bite blocks are created from dental impression material. The dental impression bite block has a better surface for sustained use, and it is very helpful for clients with limited motor control.
The client may need a bite block when the contribution of the mandible cannot be distinguished from that of the lips or tongue during articulation. For example, in situations in which the tongue should be the dominant articulator instead of the mandible, the therapist might want to strengthen the tongue. One exercise for strengthening the tongue is to (a) place a bite block between the client's molars, (b) use a tongue depressor for resistance, and (c) ask the client to push the tongue up toward the roof of the mouth against the tongue depressor.
Answer to Question 2
Articulation is the process of joining two elements together to form a point of union. In speech science, the articulatory system brings mobile and immobile articulators together for the purpose of shaping the sounds of speech. Mobile articulators are the tongue, lower jaw (mandible), velum (soft palate), lips, and cheeks. Immobile articulators are the alveolar ridge of the upper jaw (maxillae), hard palate, and teeth. The articulatory system is a very vital part of the communication system.