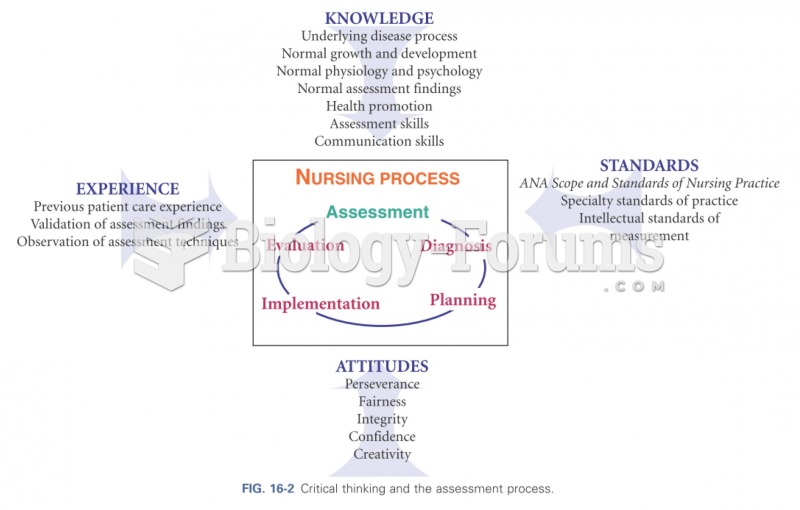
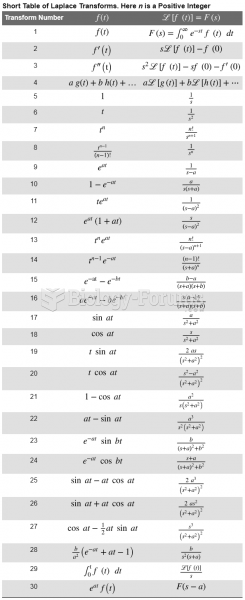
Answer to Question 1
Answer: Step 1: Identification of a problem
The decision-making process begins with a discrepancy between an existing and a desired state of affairs. An example of identifying a problem is choosing a new car.
Step 2: Identification of decision criteria
Once the manager has identified a problem that needs attention, the decision criteria important to resolving the problem must be identified. That is, managers must determine what factors are relevant in making a decision. An example of identifying decision criteria is deciding what features you need in a new car.
Step 3: Allocation of weights to the criteria
At this step, the decision maker must compare the items in order to give them the correct priority in the decision. The most important criterion is assigned the heaviest weight. Other criteria are assigned weights in comparison with that standard. Weights can be quantitativewith number valuesor determined on a qualitative scale. An example of weighting decision criteria is ranking the features of a new car in order of their importance.
Step 4: Development of alternatives
The fourth step requires the decision maker to use the criteria to develop a list of possible alternatives that may solve the problem. An example of developing alternatives is making a list of possible new cars.
Answer to Question 2
Answer: TRUE
Explanation: Confirmation bias means that the decision maker has already made up his or her mind and is seeking only the information that will confirm that position.