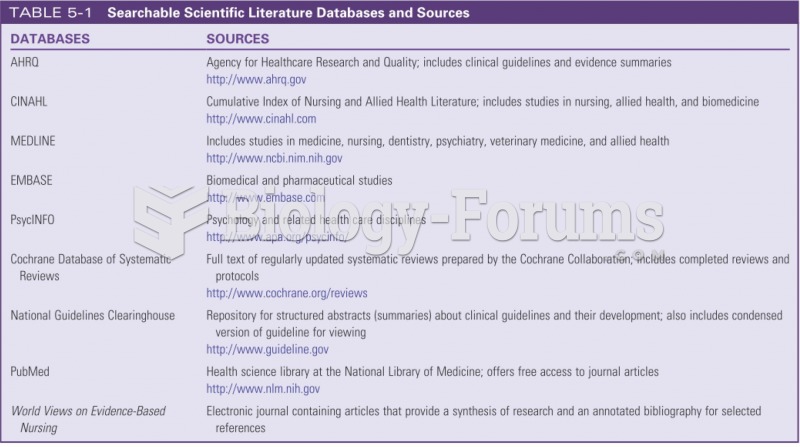
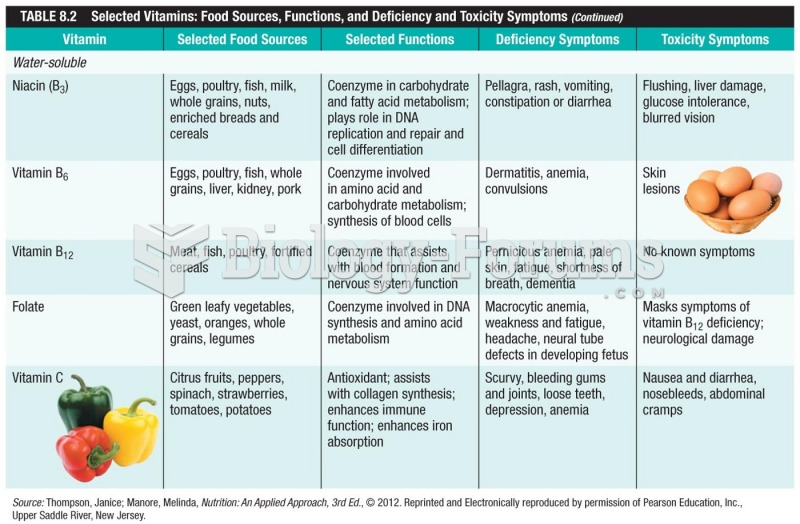
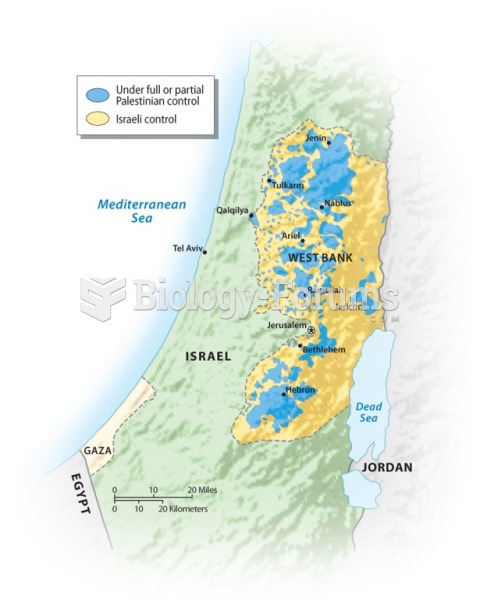
Answer to Question 1
Answer: Based on an actual investment firm, this case chronicles the challenges facing the head of a very conservative organization (Dan), who hires a strong-willed, highly successful senior staff member (Mike) with a very different investment philosophy. The resulting conflict is extremely disruptive, eventually leading to Mike and EPI parting company.
All four causes of conflict discussed in the chapter are present in this case. Mike and Dan have very different personal interests. They are operating on different sources of information (or at least different interpretations of the same informationmarket projections). Their roles are incompatible in the sense that Mike was brought in to interject new ideas. And their disagreements are exacerbated by limited staff resources and conflicting signals from their investors (environmental stress). Some might argue that it is easier to manage multisource conflicts because they allow more points of leverage (e.g., if you cannot resolve the interpersonal difference problem now, at least you can correct the error in information usage).
Answer to Question 2
When the parties involved in a conflict are unable to resolve the problem, a mediator is generally required to cool down the dispute, reestablish constructive communication, and help the parties reconcile their differences. The mediator should follow the following guidelines in identifying the problem. (1) Acknowledge that a conflict exists and propose a problem-solving approach for resolving it. One of the first decisions of the mediator is to determine whether to convene a joint problem-solving session or meet separately with the parties first. In making this decision, the mediator should determine the current position of the parties, the nature of the relationship, and the nature of the problem (see Table 7 for additional information). (2) In seeking out the perspective of both parties, maintain a neutral, impartial posture regarding the parties and of the issue if possible. (3) Serve as a facilitator, not as a judge. (4) Manage the discussion to ensure fairness; keep the discussion issue oriented, not personality oriented. The following guidelines apply in generating a solution. (1) Explore options by focusing on interests, not positions. (2) Make sure the parties fully understand and support the agreed-upon solution and establish follow-up procedures.