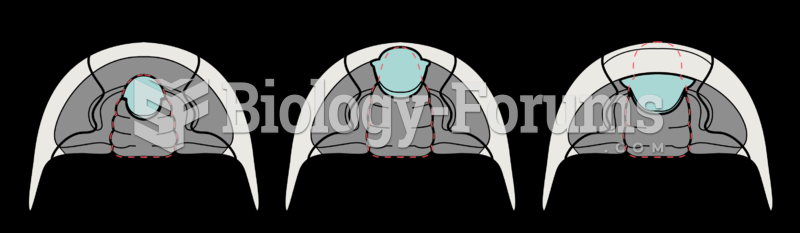
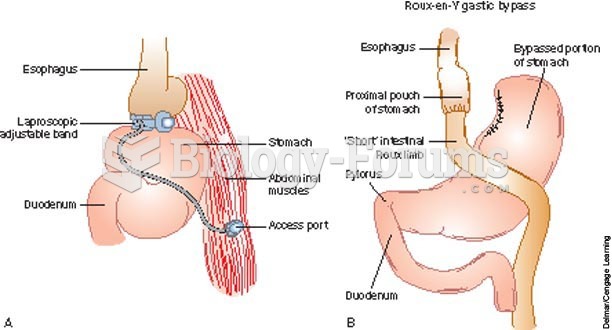
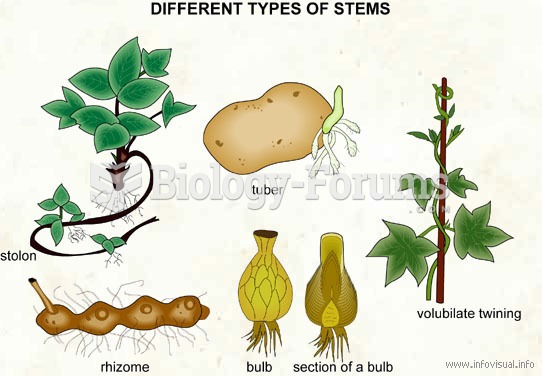
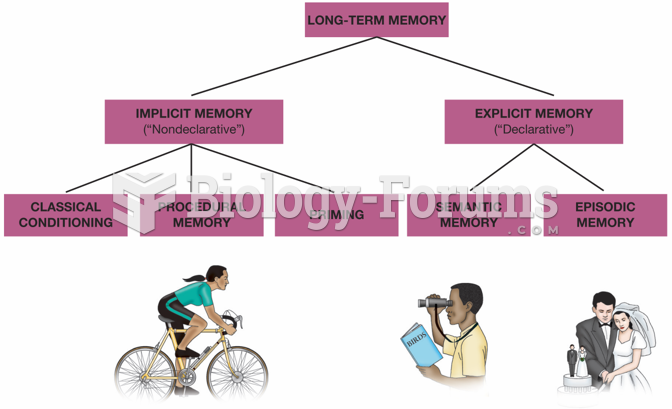
|
|
|
As many as 28% of hospitalized patients requiring mechanical ventilators to help them breathe (for more than 48 hours) will develop ventilator-associated pneumonia. Current therapy involves intravenous antibiotics, but new antibiotics that can be inhaled (and more directly treat the infection) are being developed.
Cucumber slices relieve headaches by tightening blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the area, and relieving pressure.
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.
Warfarin was developed as a consequence of the study of a strange bleeding disorder that suddenly occurred in cattle on the northern prairies of the United States in the early 1900s.
The average person is easily confused by the terms pharmaceutics and pharmacology, thinking they are one and the same. Whereas pharmaceutics is the science of preparing and dispensing drugs (otherwise known as the science of pharmacy), pharmacology is the study of medications.