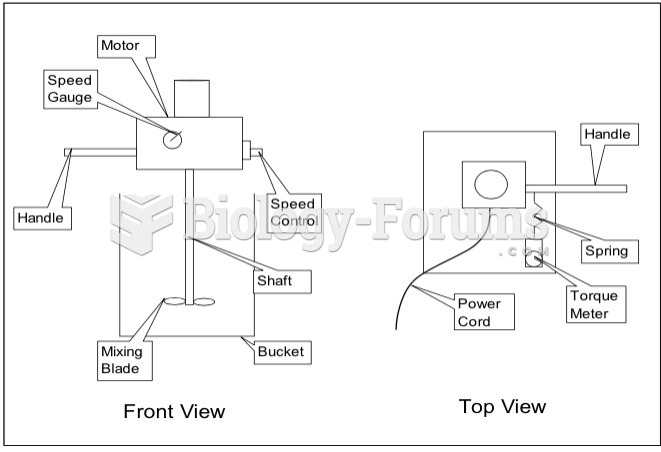
|
|
|
Hippocrates noted that blood separates into four differently colored liquids when removed from the body and examined: a pure red liquid mixed with white liquid material with a yellow-colored froth at the top and a black substance that settles underneath; he named these the four humors (for blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile).
The FDA recognizes 118 routes of administration.
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
Russia has the highest death rate from cardiovascular disease followed by the Ukraine, Romania, Hungary, and Poland.
More than 20 million Americans cite use of marijuana within the past 30 days, according to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). More than 8 million admit to using it almost every day.