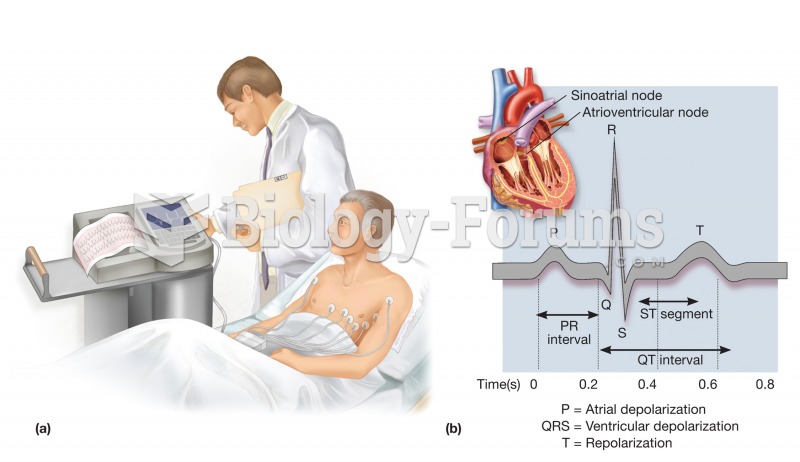
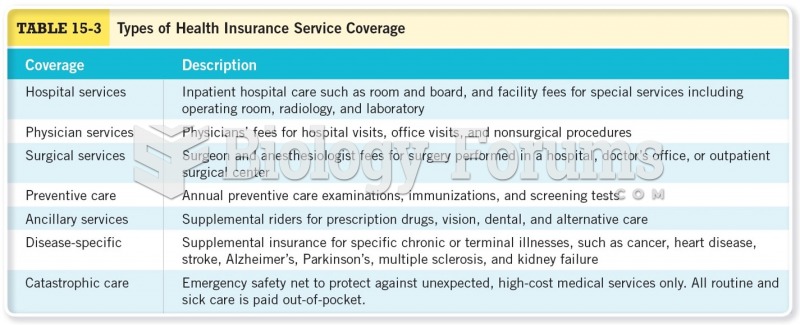
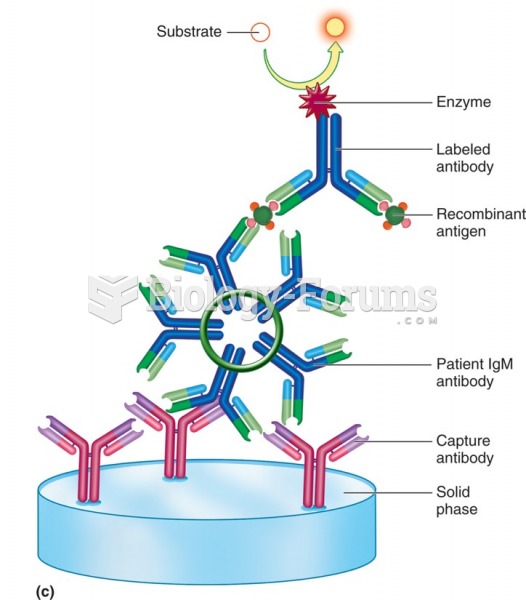
|
|
|
People who have myopia, or nearsightedness, are not able to see objects at a distance but only up close. It occurs when the cornea is either curved too steeply, the eye is too long, or both. This condition is progressive and worsens with time. More than 100 million people in the United States are nearsighted, but only 20% of those are born with the condition. Diet, eye exercise, drug therapy, and corrective lenses can all help manage nearsightedness.
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.
Lower drug doses for elderly patients should be used first, with titrations of the dose as tolerated to prevent unwanted drug-related pharmacodynamic effects.
Although the Roman numeral for the number 4 has always been taught to have been "IV," according to historians, the ancient Romans probably used "IIII" most of the time. This is partially backed up by the fact that early grandfather clocks displayed IIII for the number 4 instead of IV. Early clockmakers apparently thought that the IIII balanced out the VIII (used for the number 8) on the clock face and that it just looked better.
According to the CDC, approximately 31.7% of the U.S. population has high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad cholesterol" levels.