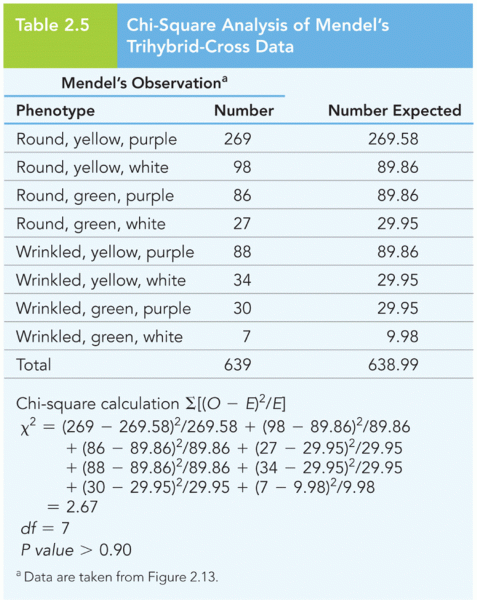
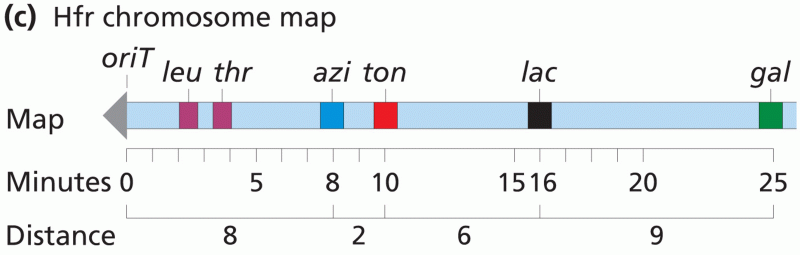
Answer to Question 1
ANS: B
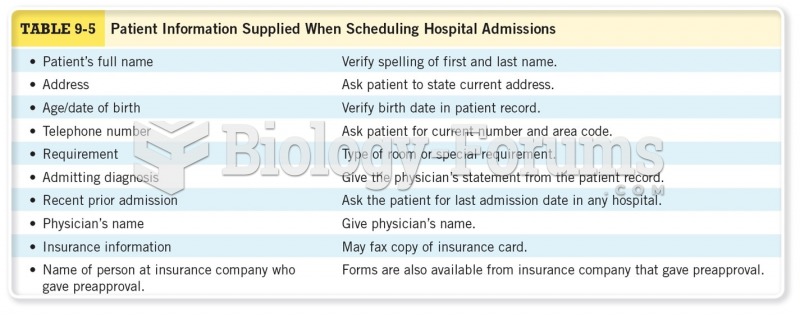
Before data collection begins, the researcher develops or adapts forms on which to record data. These forms can be used to record demographic data, information from the patient record, observations, or values from physiological measures. The researcher also might need to collect other data that may be extraneous or confounding variables such as the subject's physician, stage of illness, length of illness or hospitalization, complications, date of data collection, time of day and day of week of data collection, and any untoward events that occur during the data collection period. Data collection forms must be designed so that the data are easily recorded. If a form isn't working, design a better form. Data collection forms themselves do not need institutional review board (IRB) approvalthe information to be collected is what the IRB approves.
Answer to Question 2
ANS: A, B, C, E
A systematic review is a structured, comprehensive synthesis of the research literature to determine the best research evidence available to address a health care question. A systematic review involves identifying, locating, appraising, and synthesizing quality research evidence for expert clinicians to use to promote an EBP. Systematic reviews are often conducted by two or more researchers and/or clinicians in a selected area of interest to determine the best research knowledge in that area. Systematic reviews need to be conducted with rigorous research methodology to promote the accuracy of the findings and minimize the reviewers' bias. A systemic review or meta-analysis is best directed by a relevant clinical question that focuses the review process and promotes the development of a quality synthesis of research evidence. One of the most common formats used to organize a systematic review is the PICO or PICOS format described in the Cochran Handbook. PICOS are (1) population (or sample), (2) intervention, (3) comparison group or condition, (4) outcomes, and (5) study design. Naturally occurring interventions indicate a non-interventional design; the researcher enacts the research intervention.