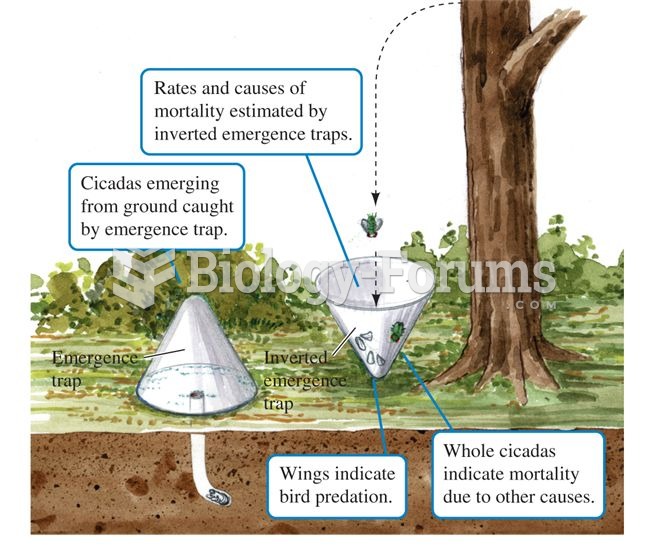
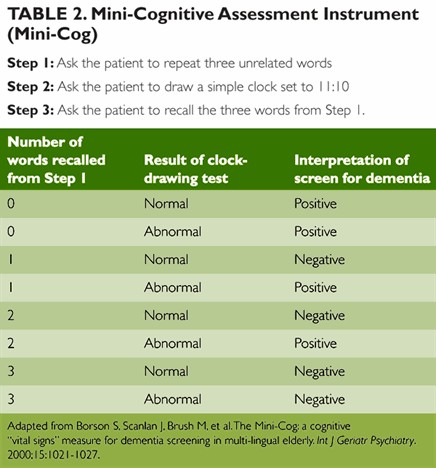
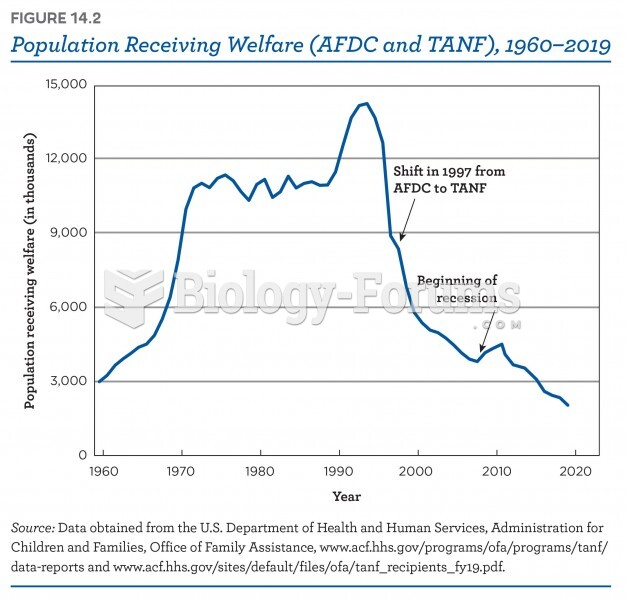
|
|
|
The tallest man ever known was Robert Wadlow, an American, who reached the height of 8 feet 11 inches. He died at age 26 years from an infection caused by the immense weight of his body (491 pounds) and the stress on his leg bones and muscles.
Over time, chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections can progress to advanced liver disease, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Unlike other forms, more than 80% of hepatitis C infections become chronic and lead to liver disease. When combined with hepatitis B, hepatitis C now accounts for 75% percent of all cases of liver disease around the world. Liver failure caused by hepatitis C is now leading cause of liver transplants in the United States.
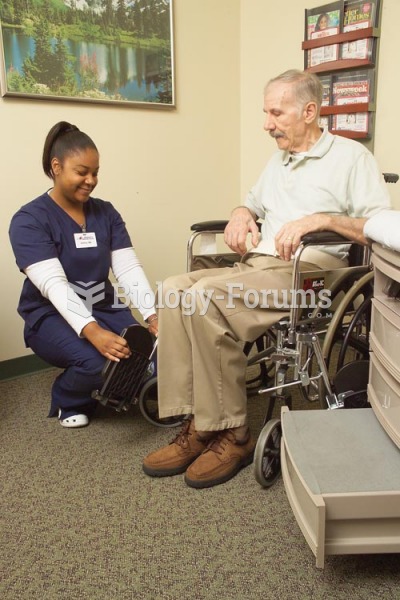
Vital signs (blood pressure, temperature, pulse rate, respiration rate) should be taken before any drug administration. Patients should be informed not to use tobacco or caffeine at least 30 minutes before their appointment.
There are 20 feet of blood vessels in each square inch of human skin.
Malaria mortality rates are falling. Increased malaria prevention and control measures have greatly improved these rates. Since 2000, malaria mortality rates have fallen globally by 60% among all age groups, and by 65% among children under age 5.