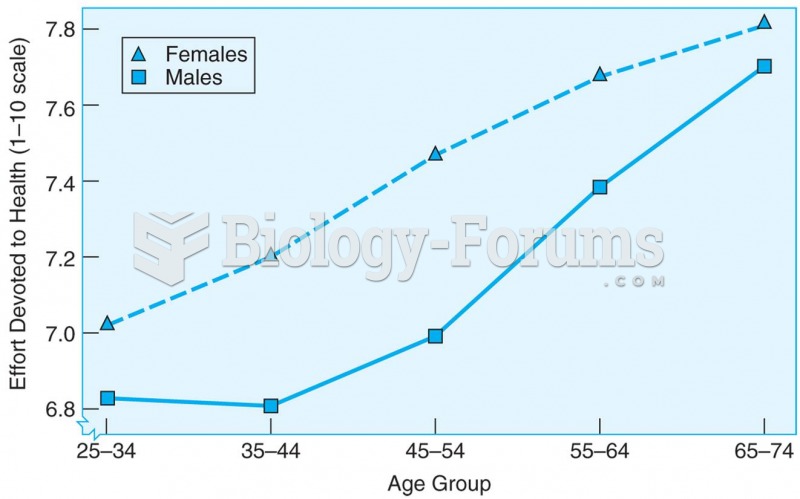
|
|
|
Automated pill dispensing systems have alarms to alert patients when the correct dosing time has arrived. Most systems work with many varieties of medications, so patients who are taking a variety of drugs can still be in control of their dose regimen.
As of mid-2016, 18.2 million people were receiving advanced retroviral therapy (ART) worldwide. This represents between 43–50% of the 34–39.8 million people living with HIV.
Cocaine was isolated in 1860 and first used as a local anesthetic in 1884. Its first clinical use was by Sigmund Freud to wean a patient from morphine addiction. The fictional character Sherlock Holmes was supposed to be addicted to cocaine by injection.
Computer programs are available that crosscheck a new drug's possible trade name with all other trade names currently available. These programs detect dangerous similarities between names and alert the manufacturer of the drug.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released reports detailing the deaths of infants (younger than 1 year of age) who died after being given cold and cough medications. This underscores the importance of educating parents that children younger than 2 years of age should never be given over-the-counter cold and cough medications without consulting their physicians.