Answer to Question 1
Answer: Heredity cannot be controlled; once you are conceived, your genetic composition and family history have been determined. Likewise, you cannot control your age.
The majority of our environmental conditions are beyond our control, such as global warming and natural disasters (although we can control our response to these factors by being aware and prepared).
The development of resistant organisms is beyond our control. We can reduce our personal risk by taking antibiotics only when necessary (not for viral infections) and by completing all antibiotic therapies as directed.
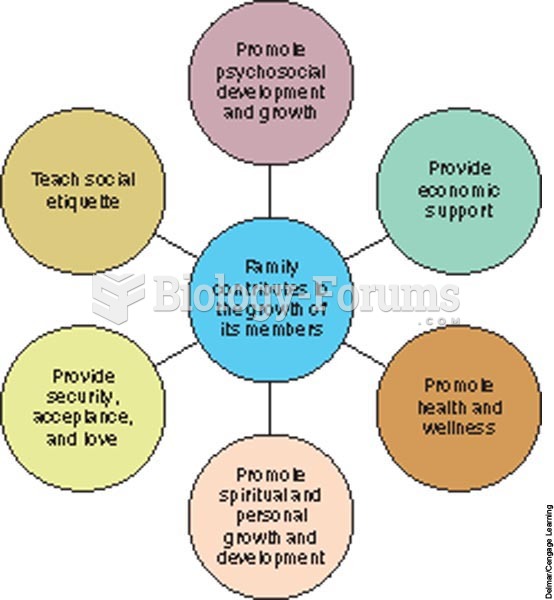
The factors we can control have the greatest impact on our overall healththe behavioral factors:
Control stress. We cannot eliminate stressors, but we can control our responses to stressors, thus decreasing the effects of chronic stress such as obesity, heart disease, and decreased immunity.
Eat a healthy diet, be physically fit, and be well-rested.
Limit/avoid high-risk behaviors such as using and abusing legal or illegal drug substances, including tobacco and alcohol, mixing drinking and driving, and having unprotected sex.
Practice good personal hygiene, including good hand-washing practices.
Answer to Question 2
Answer: Three conditions must be present at the same time to develop disease from exposure to a microorganism.
1) The agent must be able to transmit the pathogen. In other words, there must be contactthrough broken skin, inhalation, and so forthbetween the pathogen and the interior of the human body. Skin, for example, is the body's first defense: pathogens can gain entry to the body via cut or burned skin, but are not able to gain entry in a person with intact skin.
2) The host must be susceptible; that is, vulnerable in some way to the infection. Most obviously, the host's body temperature, chemistry, and cellular make-up must be hospitable to the pathogen involved. This explains why, for example, a certain type of influenza that is pathogenic in dogs may not be pathogenic in humans. Moreover, within any given community, some people have a strong immune system, whereas othersincluding the very young, the very old, pregnant women, and people who are illhave a compromised immune system unable to destroy the pathogen before it replicates to cause disease.
3) The environment must allow for the pathogen's survival. Factors such as temperature, light, and moisture must be hospitable to the pathogen. Pathogenic microorganisms in contaminated foods cannot reproduce in your freezer, for example, but can replicate quickly in the same food left out on your kitchen counter.