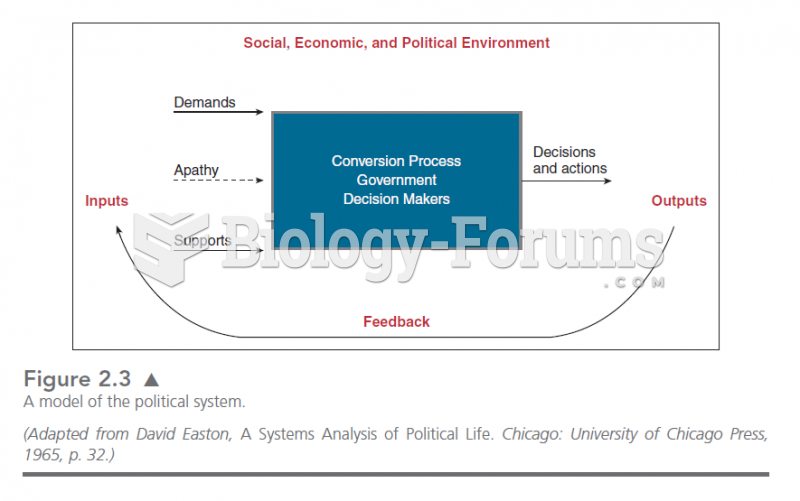
Answer to Question 1
Computerized warning systems can be used to prevent adverse drug events (ADEs). Serious ADEs occur in about 7 percent of patients admitted to hospitals. Many ADEs are caused by a physician prescribing either the wrong drug or the wrong dosage, because of lack of knowledge regarding either the patient or the drug. In 1994, a computerized warning system was designed and put into place in one hospital. The hospital already had a database with patient information; the existing system warned of a patient's specific drug allergy and of adverse drug interactions. The new alert system added warnings of other likely ADEs.
In July 2006, Preventing Medical Errors stressed that medication errors are still a serious problem, harming 1.5 million people per year. Several thousand die each year. With the aging population, more medications are prescribed, and more errors are made. Like the 1999 report To Err is Human, the 2006 report recommended the use of e-prescribing and electronic health records (EHRs).
The adoption of EHRs and e-prescribing are important steps in decreasing medication errors and reconciliation errors. One study showed that a computerized physician order entry system (CPOE) could prevent 64.4 percent of prescribing errors. A 2008 retrospective review of 10 studies found that CPOE and clinical decision support decreased ADEs in half the studies. Under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 and the Medicare Improvements for Patients and Providers Act of 2008, incentives have been established for adopting certified EHRs and e-prescribing. The e-prescribing program provides monetary incentives from 2009 to 2013 (2 percent in 2009 and 2010, 1 percent in 2011 and 2012, and 0.5 percent in 2012) and penalties from 2012 and 2014 (1 percent in 2012, 1.5 percent in 2013, and 2 percent in 2014). This looks like an error, but the incentives and penalties seem to overlap. There are conflicts between these two incentive programs. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) is attempting to integrate the two programs, and in 2009, CMS paid 148 million in incentives. Unlike the EHR program, the e-prescribing program lacks certification.
Health information technology is important in preventing medication reconciliation errors. Medication reconciliation concerns identifying the most accurate list of a patient's medications. These errors typically occur when a patient changes statusthat is, is admitted to, moved within, or released from a hospital. Between September 2004 and July 2005 in the United States, there were 2,022 reports of medication reconciliation errors. Two-thirdsresulted from transfer within the facility, another 22 occurred at patient admission, and 12...at discharge. The Institute for Healthcare Improvement estimated that as much as 50 of medication errors and 20 of ADEs in hospitals result from mismanaged medication reconciliation. EHRscould makereconciliation errors nearly nonexistent. CPOE integrated with EHR would make patient history available at all times and in all places. The records would also be legible.
Answer to Question 2
E