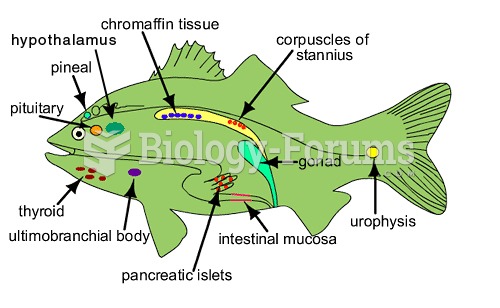
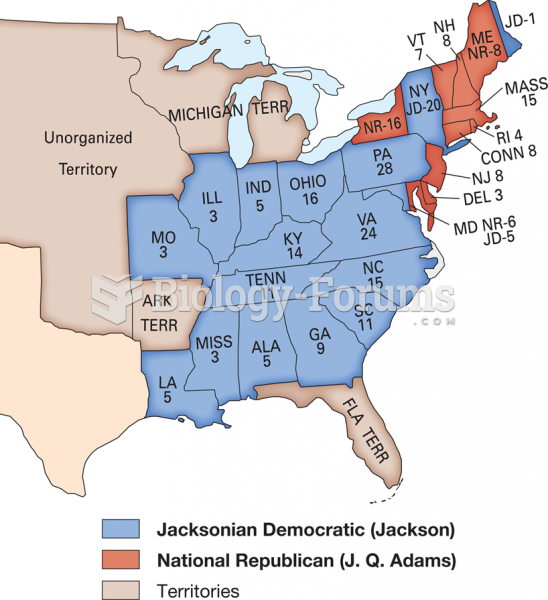
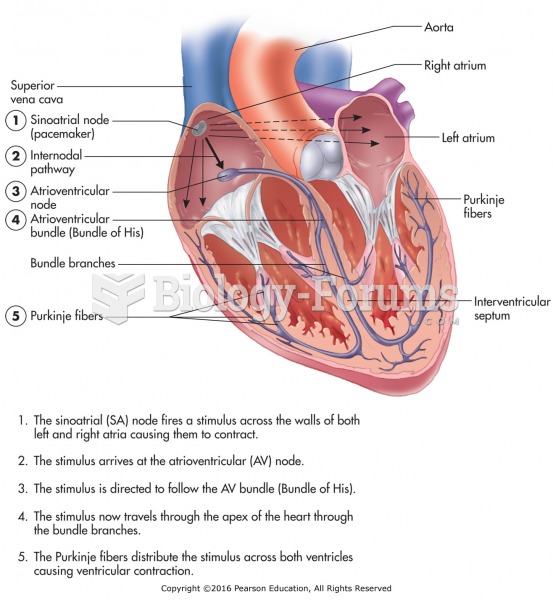
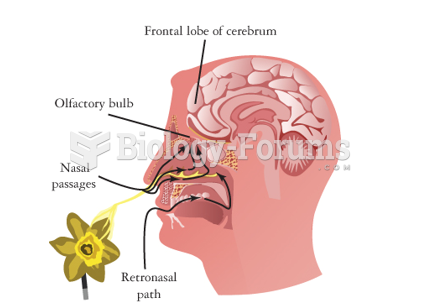
|
|
|
Malaria was not eliminated in the United States until 1951. The term eliminated means that no new cases arise in a country for 3 years.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%.
Earwax has antimicrobial properties that reduce the viability of bacteria and fungus in the human ear.
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.
Over time, chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections can progress to advanced liver disease, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Unlike other forms, more than 80% of hepatitis C infections become chronic and lead to liver disease. When combined with hepatitis B, hepatitis C now accounts for 75% percent of all cases of liver disease around the world. Liver failure caused by hepatitis C is now leading cause of liver transplants in the United States.