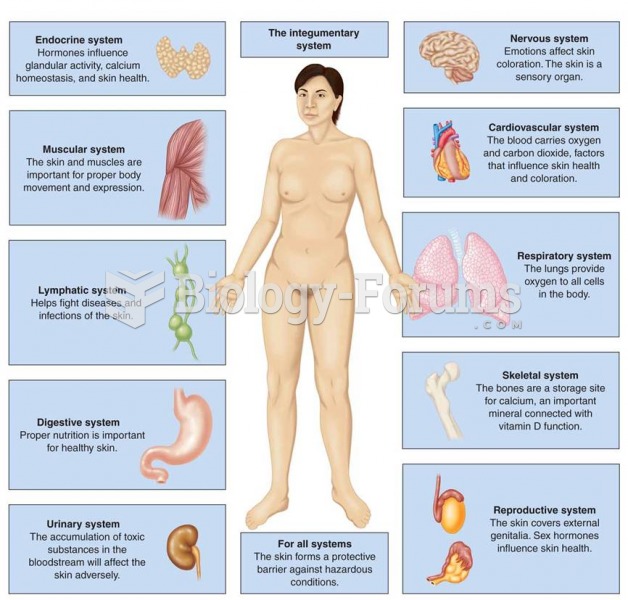
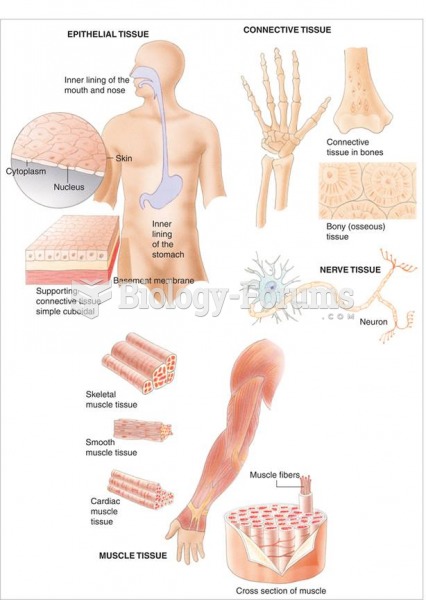
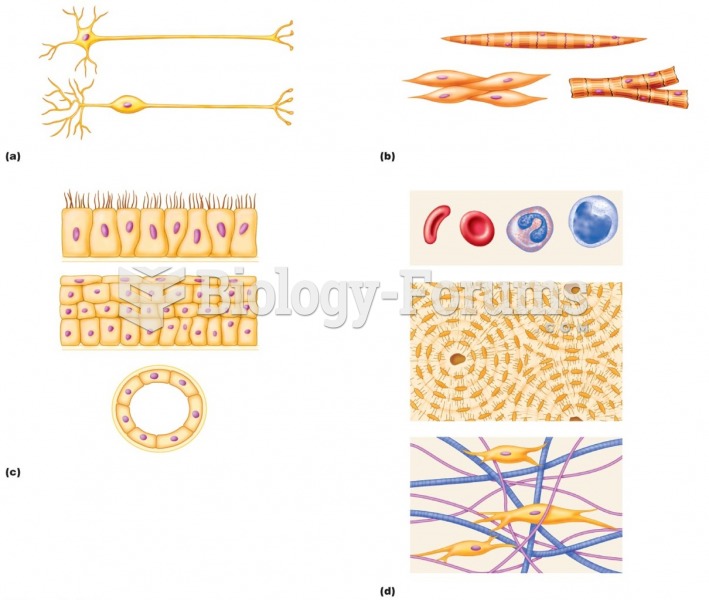
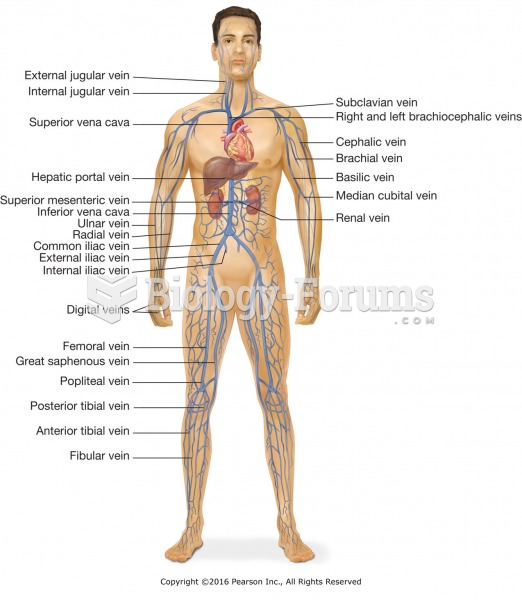
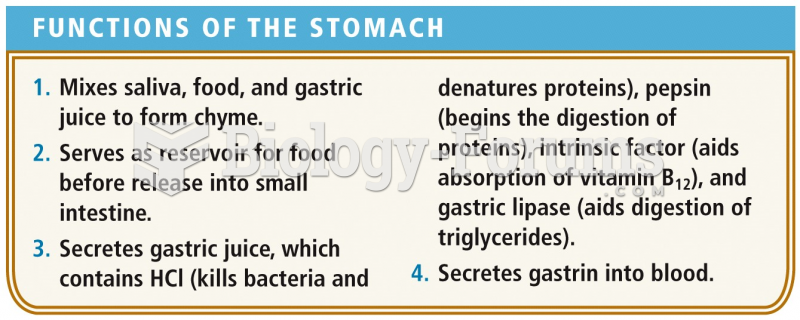
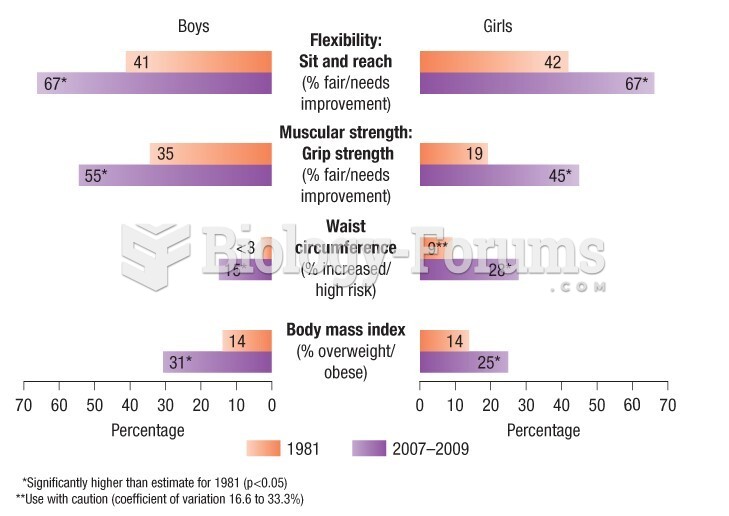
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.
Did you know?
The term pharmacology is derived from the Greek words pharmakon("claim, medicine, poison, or remedy") and logos ("study").
Did you know?
When blood is exposed to air, it clots. Heparin allows the blood to come in direct contact with air without clotting.
Did you know?
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
Did you know?
Atropine was named after the Greek goddess Atropos, the oldest and ugliest of the three sisters known as the Fates, who controlled the destiny of men.