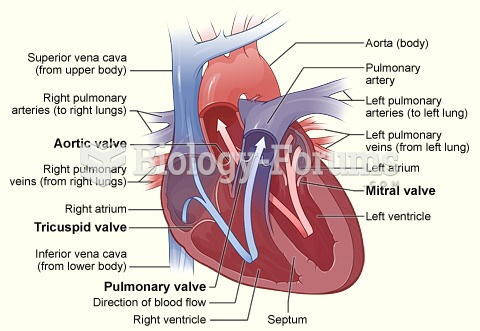
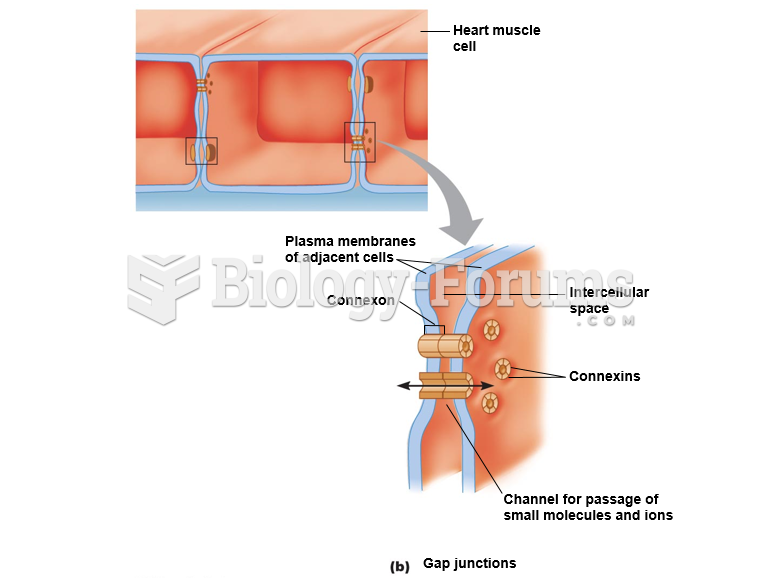
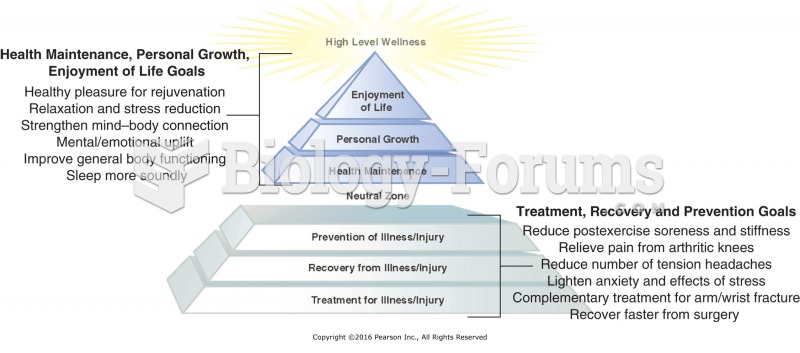
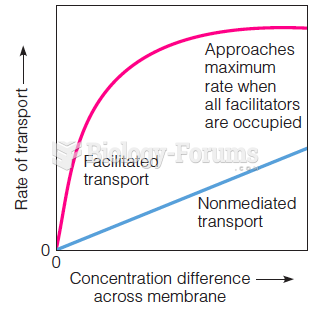
|
|
|
Anti-aging claims should not ever be believed. There is no supplement, medication, or any other substance that has been proven to slow or stop the aging process.
Most childhood vaccines are 90–99% effective in preventing disease. Side effects are rarely serious.
Parkinson's disease is both chronic and progressive. This means that it persists over a long period of time and that its symptoms grow worse over time.
Automated pill dispensing systems have alarms to alert patients when the correct dosing time has arrived. Most systems work with many varieties of medications, so patients who are taking a variety of drugs can still be in control of their dose regimen.
It is important to read food labels and choose foods with low cholesterol and saturated trans fat. You should limit saturated fat to no higher than 6% of daily calories.