|
|
|
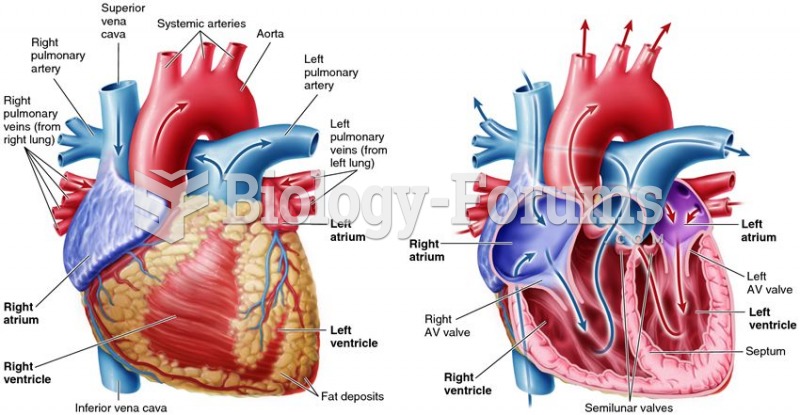
Chronic necrotizing aspergillosis has a slowly progressive process that, unlike invasive aspergillosis, does not spread to other organ systems or the blood vessels. It most often affects middle-aged and elderly individuals, spreading to surrounding tissue in the lungs. The disease often does not respond to conventionally successful treatments, and requires individualized therapies in order to keep it from becoming life-threatening.
The use of salicylates dates back 2,500 years to Hippocrates's recommendation of willow bark (from which a salicylate is derived) as an aid to the pains of childbirth. However, overdosage of salicylates can harm body fluids, electrolytes, the CNS, the GI tract, the ears, the lungs, the blood, the liver, and the kidneys and cause coma or death.
Fungal nail infections account for up to 30% of all skin infections. They affect 5% of the general population—mostly people over the age of 70.
The tallest man ever known was Robert Wadlow, an American, who reached the height of 8 feet 11 inches. He died at age 26 years from an infection caused by the immense weight of his body (491 pounds) and the stress on his leg bones and muscles.
A serious new warning has been established for pregnant women against taking ACE inhibitors during pregnancy. In the study, the risk of major birth defects in children whose mothers took ACE inhibitors during the first trimester was nearly three times higher than in children whose mothers didn't take ACE inhibitors. Physicians can prescribe alternative medications for pregnant women who have symptoms of high blood pressure.