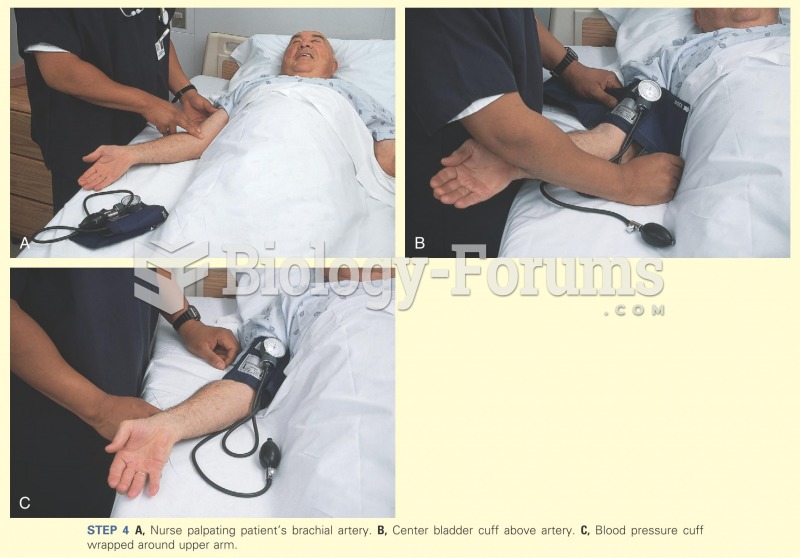
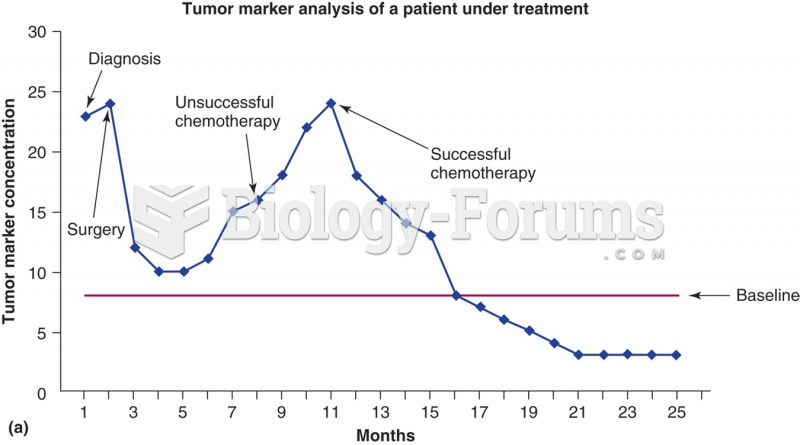
|
|
|
Once thought to have neurofibromatosis, Joseph Merrick (also known as "the elephant man") is now, in retrospect, thought by clinical experts to have had Proteus syndrome. This endocrine disease causes continued and abnormal growth of the bones, muscles, skin, and so on and can become completely debilitating with severe deformities occurring anywhere on the body.
The use of salicylates dates back 2,500 years to Hippocrates's recommendation of willow bark (from which a salicylate is derived) as an aid to the pains of childbirth. However, overdosage of salicylates can harm body fluids, electrolytes, the CNS, the GI tract, the ears, the lungs, the blood, the liver, and the kidneys and cause coma or death.
More than 4.4billion prescriptions were dispensed within the United States in 2016.
According to the CDC, approximately 31.7% of the U.S. population has high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad cholesterol" levels.
Bisphosphonates were first developed in the nineteenth century. They were first investigated for use in disorders of bone metabolism in the 1960s. They are now used clinically for the treatment of osteoporosis, Paget's disease, bone metastasis, multiple myeloma, and other conditions that feature bone fragility.