|
|
|
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors, people should avoid a variety of foods, which include alcoholic beverages, bean curd, broad (fava) bean pods, cheese, fish, ginseng, protein extracts, meat, sauerkraut, shrimp paste, soups, and yeast.
The human body produces and destroys 15 million blood cells every second.
Many supplement containers do not even contain what their labels say. There are many documented reports of products containing much less, or more, that what is listed on their labels. They may also contain undisclosed prescription drugs and even contaminants.
The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen in water (H2O) is 2:1.
Studies show that systolic blood pressure can be significantly lowered by taking statins. In fact, the higher the patient's baseline blood pressure, the greater the effect of statins on his or her blood pressure.
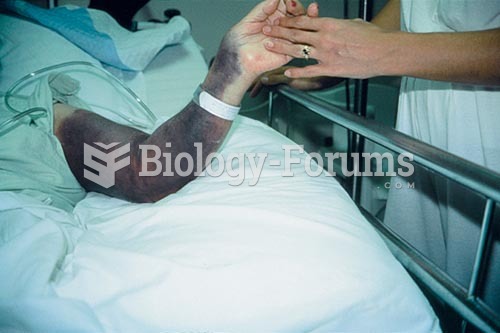 Proper placement and monitoring of an automatic blood pressure cuff will reduce the risk of injury o
Proper placement and monitoring of an automatic blood pressure cuff will reduce the risk of injury o
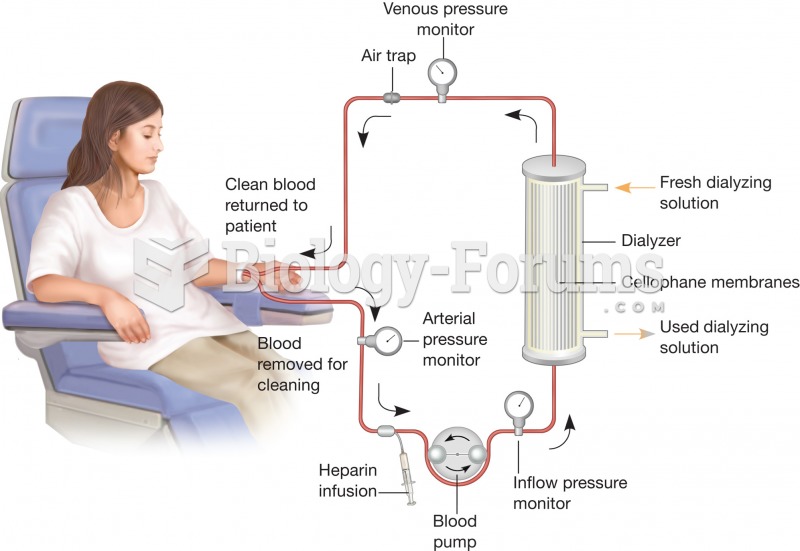 Hemodialysis. The process of hemodialysis replaces the kidney function of blood filtration by forcin
Hemodialysis. The process of hemodialysis replaces the kidney function of blood filtration by forcin