This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
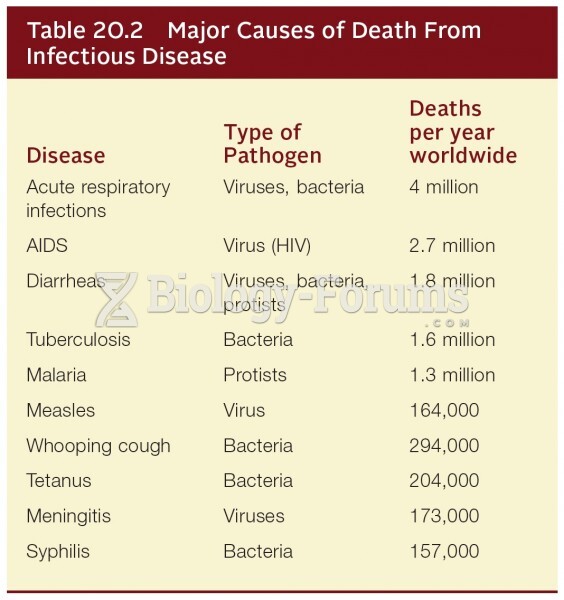
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA was discovered in 1961 in the United Kingdom. It if often referred to as a superbug. MRSA infections cause more deaths in the United States every year than AIDS.
Did you know?
One way to reduce acid reflux is to lose two or three pounds. Most people lose weight in the belly area first when they increase exercise, meaning that heartburn can be reduced quickly by this method.
Did you know?
The first oral chemotherapy drug for colon cancer was approved by FDA in 2001.
Did you know?
Asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the world. Most children who develop asthma have symptoms before they are 5 years old.
Did you know?
If all the neurons in the human body were lined up, they would stretch more than 600 miles.