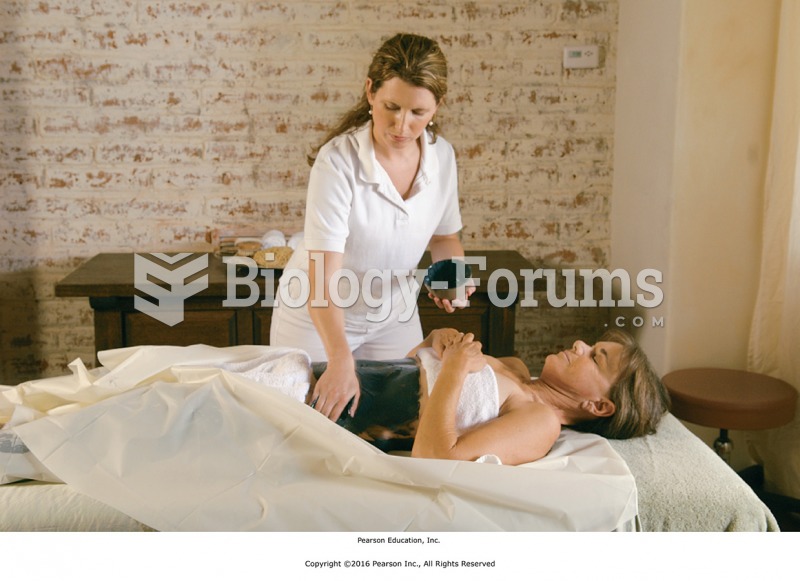
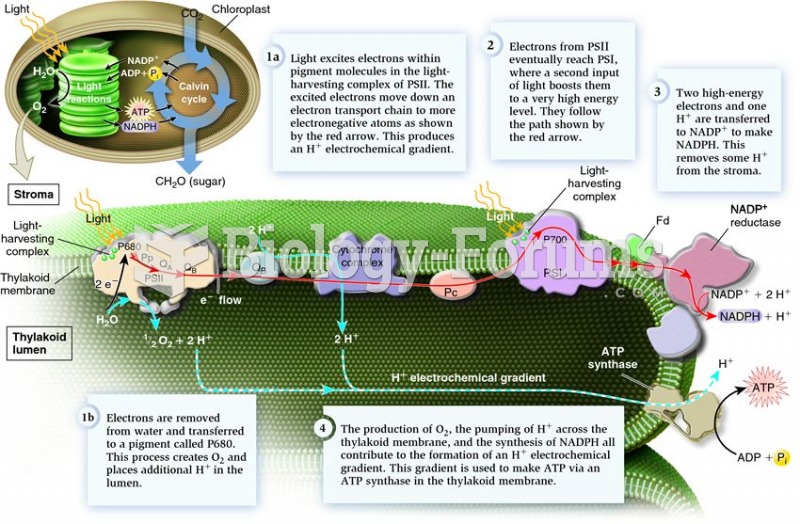
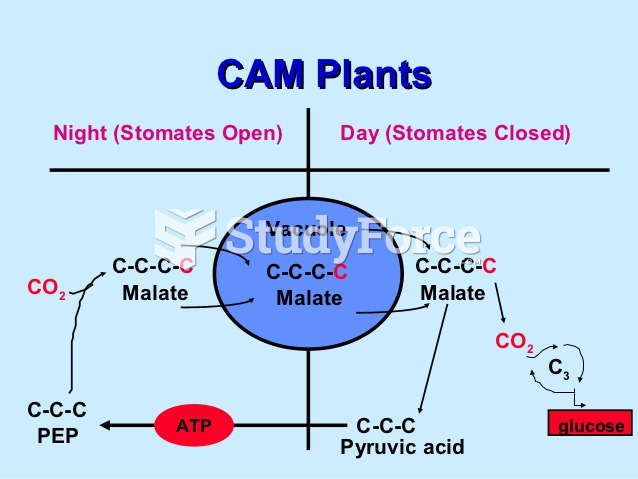
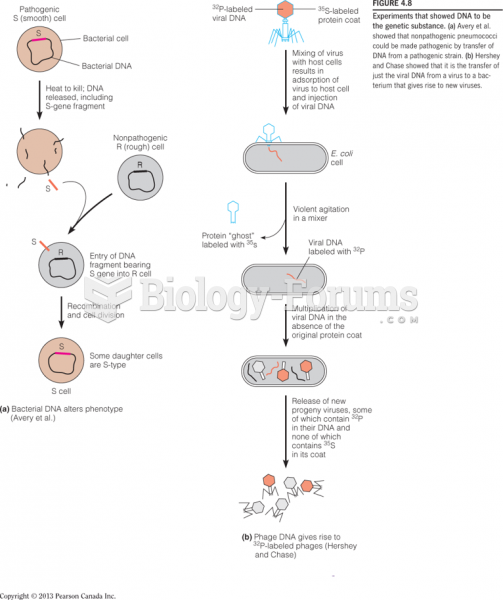
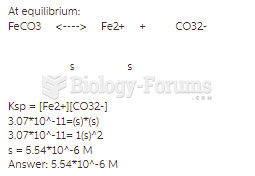
|
|
|
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
When blood is deoxygenated and flowing back to the heart through the veins, it is dark reddish-blue in color. Blood in the arteries that is oxygenated and flowing out to the body is bright red. Whereas arterial blood comes out in spurts, venous blood flows.
Hip fractures are the most serious consequences of osteoporosis. The incidence of hip fractures increases with each decade among patients in their 60s to patients in their 90s for both women and men of all populations. Men and women older than 80 years of age show the highest incidence of hip fractures.
Cytomegalovirus affects nearly the same amount of newborns every year as Down syndrome.
Signs of depression include feeling sad most of the time for 2 weeks or longer; loss of interest in things normally enjoyed; lack of energy; sleep and appetite disturbances; weight changes; feelings of hopelessness, helplessness, or worthlessness; an inability to make decisions; and thoughts of death and suicide.