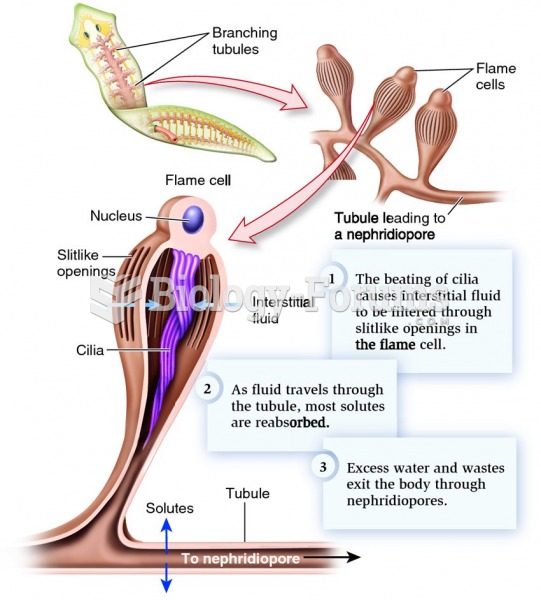
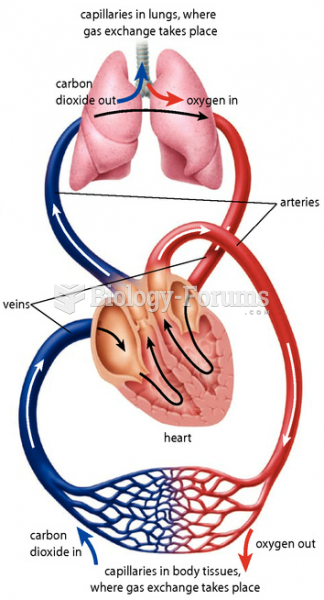
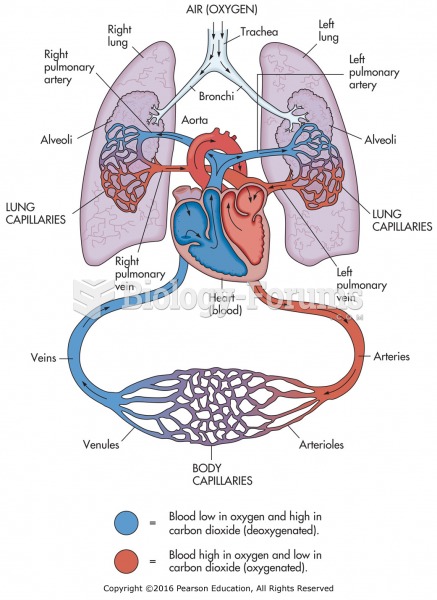
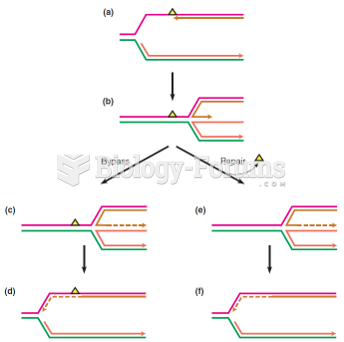
Answer to Question 1
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: Some cytokines kill pathogens directly.
Rationale 2: Some cytokines act to stimulate the inflammatory response.
Rationale 3: Cytokines are a part of the immune system and do not take over.
Rationale 4: The lymphatic system is part of the immune system that is being stimulated.
Rationale 5: The goal is to stimulate the immune response, which includes the white blood cells.
Global Rationale: Activated T cells produce huge amounts of cytokines, which are hormone-like proteins that regulate the intensity and duration of the immune response and mediate cell-to-cell communication. Some cytokines kill foreign organisms directly, whereas others induce inflammation or enhance the killing power of macrophages. Specific cytokines released by activated T cells include inter-leukins, gamma interferon, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and perforin. Some cytokines are used therapeutically to stimulate the immune system. Small amounts of cytokines are also secreted by certain macrophages, B lymphocytes, mast cells, endothelial cells, and the stromal cells of the spleen, thymus, and bone marrow. The client's immune system will not shut down or be taken over by this process. The goal is to stimulate the immune system, which increases the number of white blood cells.
Answer to Question 2
Correct Answer: 1,2,4
Rationale 1: Interferons are proteins produced in the body.
Rationale 2: Interferons have been isolated and are now available as medications for the treatment of immune disorders, viral infections, and cancer.
Rationale 3: The health care provider may well have told the client that interferon production was depressed.
Rationale 4: Interferons stimulate the activity of phagocytes and NK cells.
Rationale 5: Natural killer cells are stimulated by interferons.
Global Rationale: Interferons (IFNs) are antimicrobial proteins that are crucial components of the innate body defense system. Released by infected macrophages and lymphocytes, IFNs protect uninfected cells from the pathogen. IFNs have been isolated and are now available as medications for the treatment of immune disorders, viral infections, and cancer. Interferons do not help stimulate other cells. There is no reason to believe the patient misunderstood the physician.