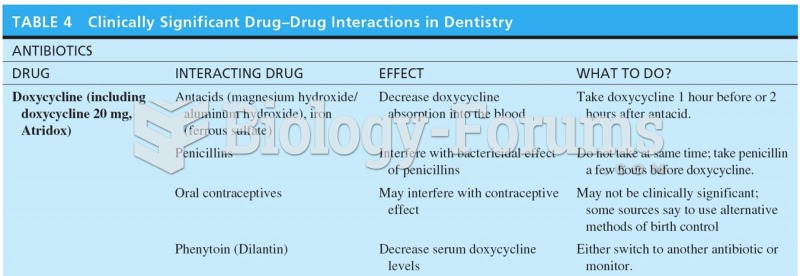
|
|
|
Though Candida and Aspergillus species are the most common fungal pathogens causing invasive fungal disease in the immunocompromised, infections due to previously uncommon hyaline and dematiaceous filamentous fungi are occurring more often today. Rare fungal infections, once accurately diagnosed, may require surgical debridement, immunotherapy, and newer antifungals used singly or in combination with older antifungals, on a case-by-case basis.
Asthma attacks and symptoms usually get started by specific triggers (such as viruses, allergies, gases, and air particles). You should talk to your doctor about these triggers and find ways to avoid or get rid of them.
Cutaneous mucormycosis is a rare fungal infection that has been fatal in at least 29% of cases, and in as many as 83% of cases, depending on the patient's health prior to infection. It has occurred often after natural disasters such as tornados, and early treatment is essential.
The lipid bilayer is made of phospholipids. They are arranged in a double layer because one of their ends is attracted to water while the other is repelled by water.
Vampire bats have a natural anticoagulant in their saliva that permits continuous bleeding after they painlessly open a wound with their incisors. This capillary blood does not cause any significant blood loss to their victims.