|
|
|
Nearly 31 million adults in America have a total cholesterol level that is more than 240 mg per dL.
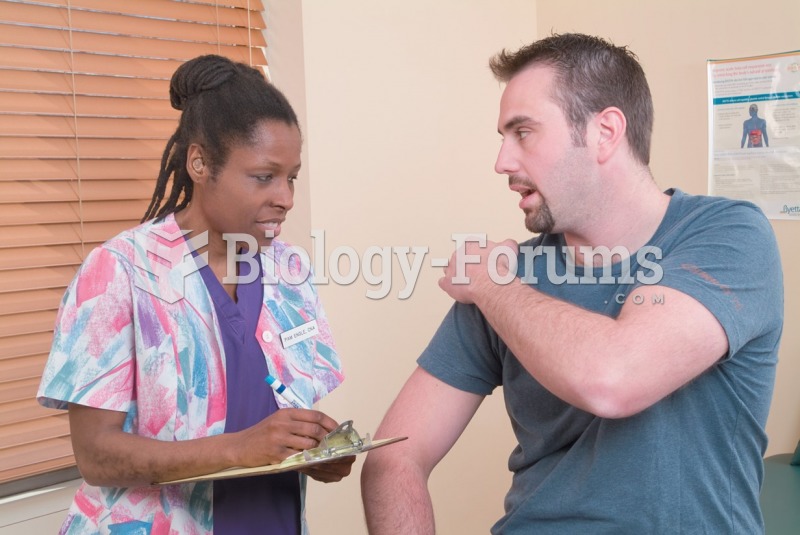
Hypertension is a silent killer because it is deadly and has no significant early symptoms. The danger from hypertension is the extra load on the heart, which can lead to hypertensive heart disease and kidney damage. This occurs without any major symptoms until the high blood pressure becomes extreme. Regular blood pressure checks are an important method of catching hypertension before it can kill you.
Sildenafil (Viagra®) has two actions that may be of consequence in patients with heart disease. It can lower the blood pressure, and it can interact with nitrates. It should never be used in patients who are taking nitrates.
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.