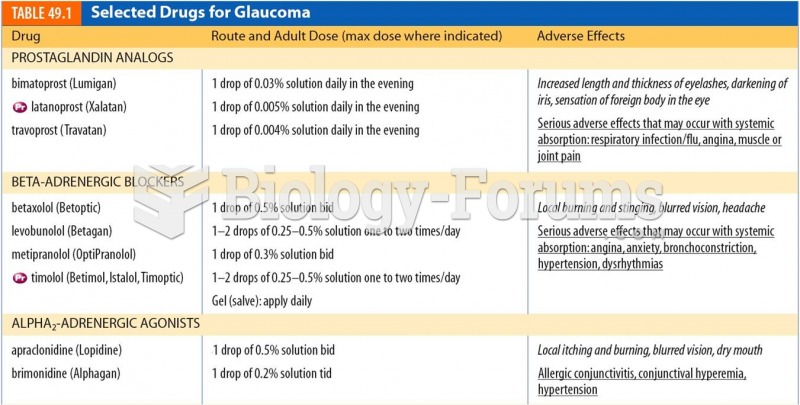
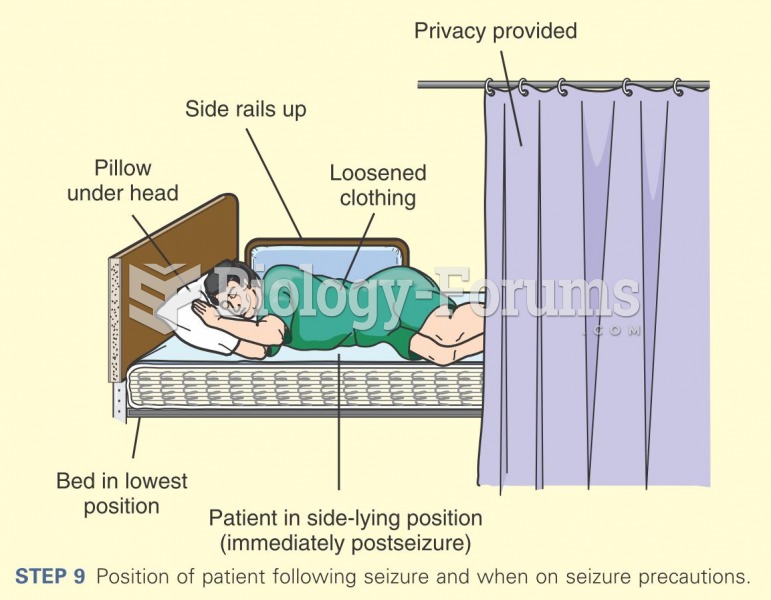
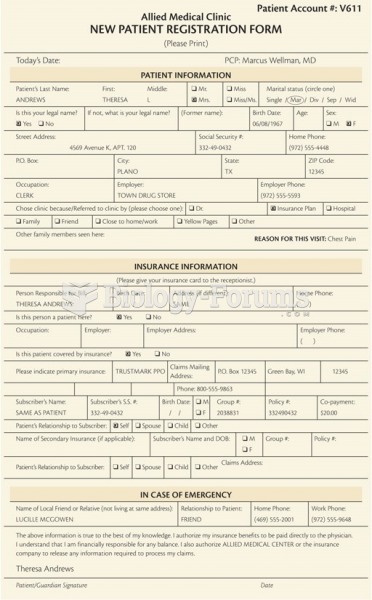
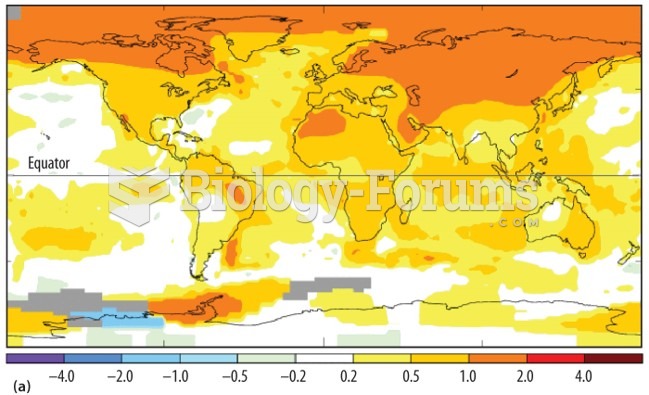
|
|
|
In Eastern Europe and Russia, interferon is administered intranasally in varied doses for the common cold and influenza. It is claimed that this treatment can lower the risk of infection by as much as 60–70%.
After 5 years of being diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, one every three patients will no longer be able to work.
Addicts to opiates often avoid treatment because they are afraid of withdrawal. Though unpleasant, with proper management, withdrawal is rarely fatal and passes relatively quickly.
Pregnant women usually experience a heightened sense of smell beginning late in the first trimester. Some experts call this the body's way of protecting a pregnant woman from foods that are unsafe for the fetus.
On average, someone in the United States has a stroke about every 40 seconds. This is about 795,000 people per year.