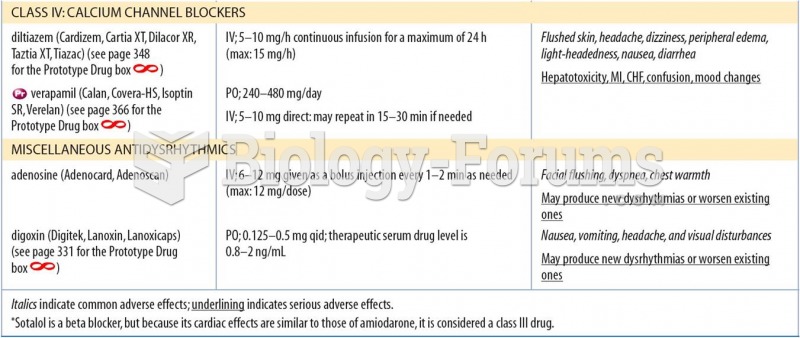
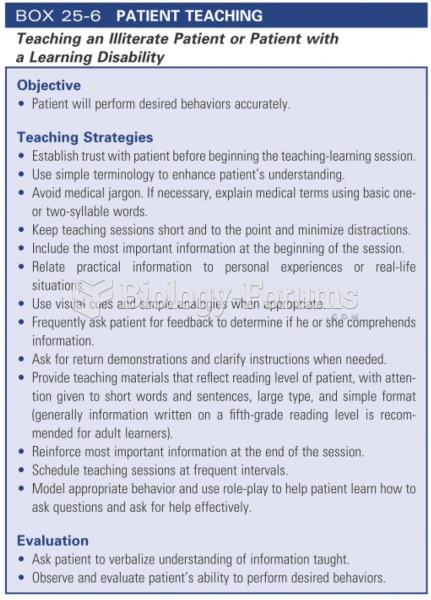
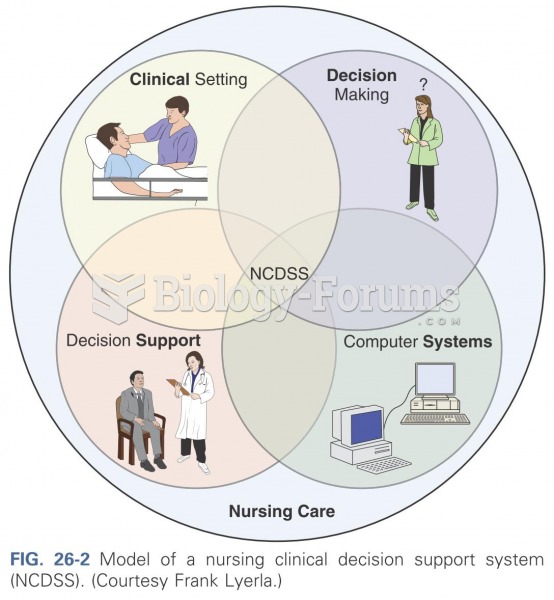
|
|
|
More than 30% of American adults, and about 12% of children utilize health care approaches that were developed outside of conventional medicine.
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.
When intravenous medications are involved in adverse drug events, their harmful effects may occur more rapidly, and be more severe than errors with oral medications. This is due to the direct administration into the bloodstream.
In Eastern Europe and Russia, interferon is administered intranasally in varied doses for the common cold and influenza. It is claimed that this treatment can lower the risk of infection by as much as 60–70%.
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.