|
|
|
In the United States, there is a birth every 8 seconds, according to the U.S. Census Bureau's Population Clock.
All patients with hyperparathyroidism will develop osteoporosis. The parathyroid glands maintain blood calcium within the normal range. All patients with this disease will continue to lose calcium from their bones every day, and there is no way to prevent the development of osteoporosis as a result.
Allergies play a major part in the health of children. The most prevalent childhood allergies are milk, egg, soy, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, and seafood.
Drug abusers experience the following scenario: The pleasure given by their drug (or drugs) of choice is so strong that it is difficult to eradicate even after years of staying away from the substances involved. Certain triggers may cause a drug abuser to relapse. Research shows that long-term drug abuse results in significant changes in brain function that persist long after an individual stops using drugs. It is most important to realize that the same is true of not just illegal substances but alcohol and tobacco as well.
Serum cholesterol testing in adults is recommended every 1 to 5 years. People with diabetes and a family history of high cholesterol should be tested even more frequently.
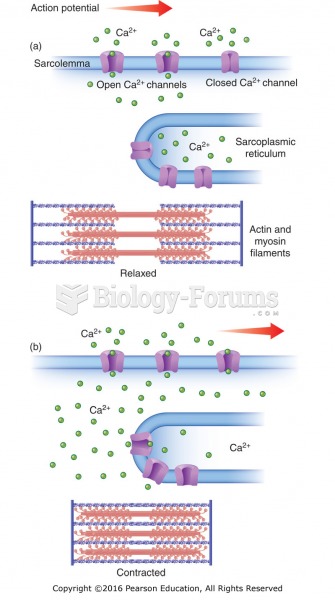 Calcium channels and muscle contraction: (a) Calcium channels open as the action potential travels ...
Calcium channels and muscle contraction: (a) Calcium channels open as the action potential travels ...
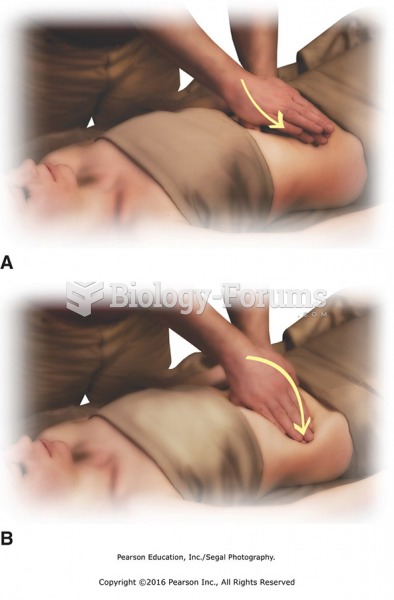 Apply petrissage to center of abdomen. Place hands palm over palm in center of the abdomen. Create ...
Apply petrissage to center of abdomen. Place hands palm over palm in center of the abdomen. Create ...