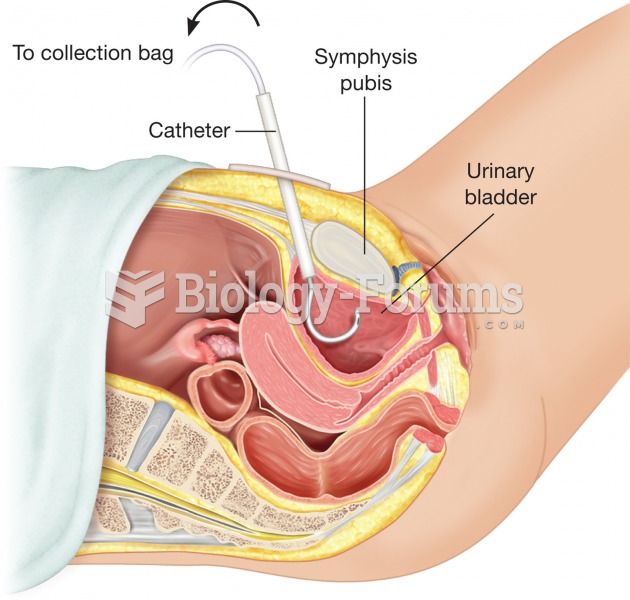
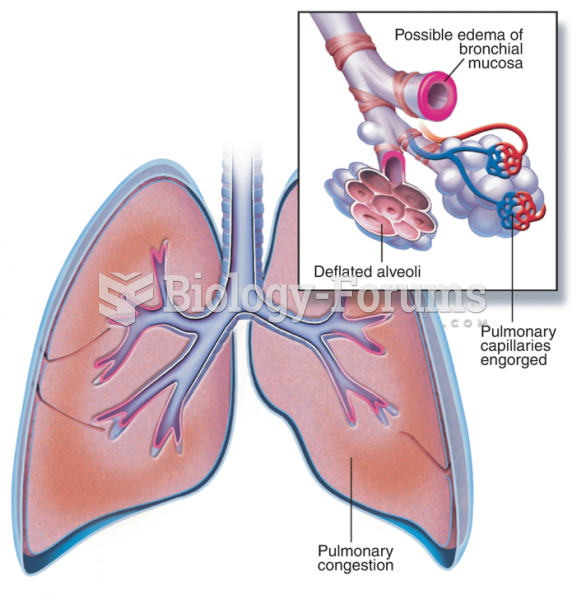
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
In inpatient settings, adverse drug events account for an estimated one in three of all hospital adverse events. They affect approximately 2 million hospital stays every year, and prolong hospital stays by between one and five days.
Did you know?
No drugs are available to relieve parathyroid disease. Parathyroid disease is caused by a parathyroid tumor, and it needs to be removed by surgery.
Did you know?
Women are 50% to 75% more likely than men to experience an adverse drug reaction.
Did you know?
It is believed that humans initially contracted crabs from gorillas about 3 million years ago from either sleeping in gorilla nests or eating the apes.
Did you know?
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.