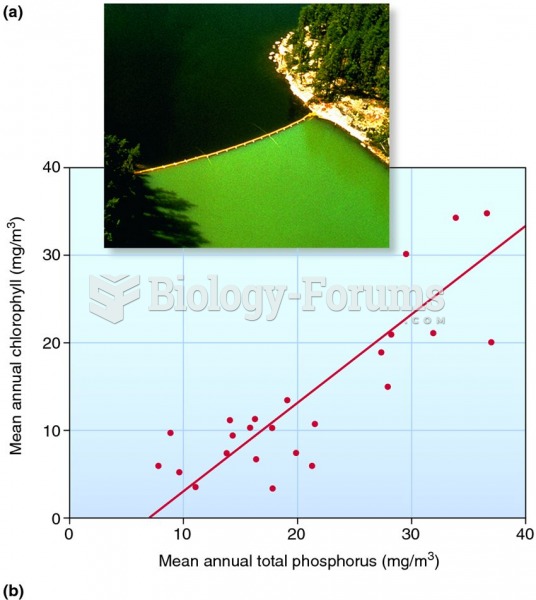
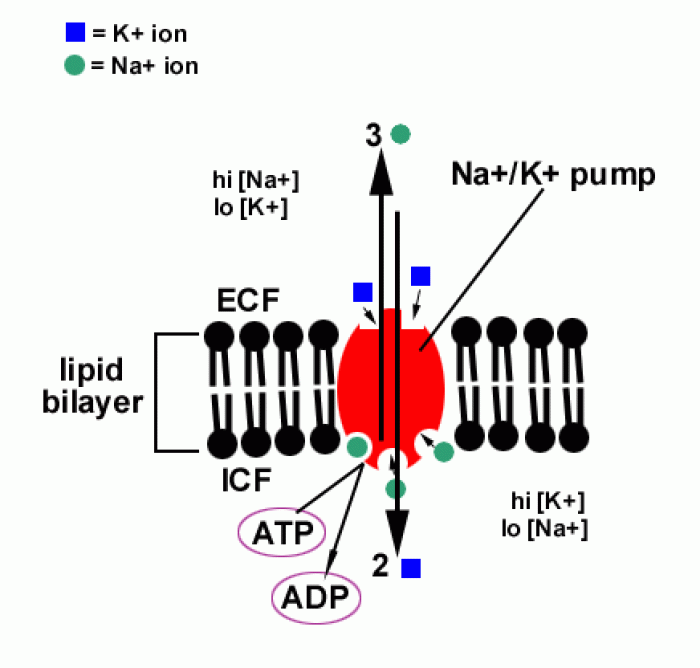
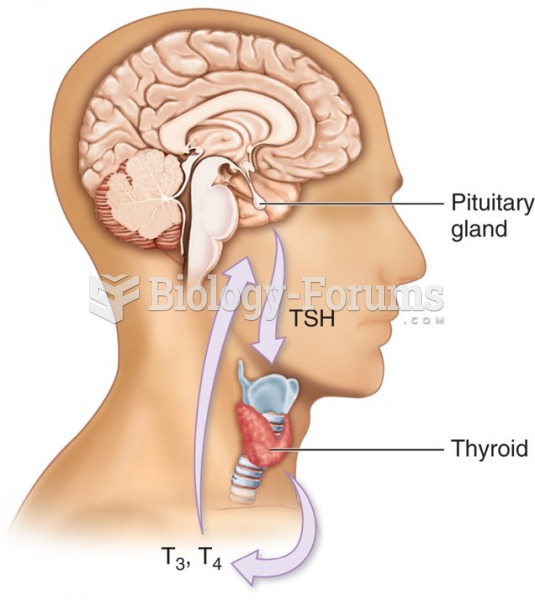
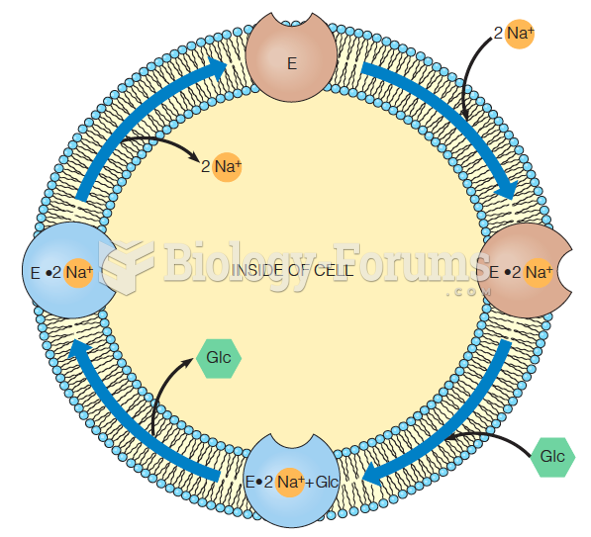
|
|
|
When intravenous medications are involved in adverse drug events, their harmful effects may occur more rapidly, and be more severe than errors with oral medications. This is due to the direct administration into the bloodstream.
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.
Children of people with alcoholism are more inclined to drink alcohol or use hard drugs. In fact, they are 400 times more likely to use hard drugs than those who do not have a family history of alcohol addiction.
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.