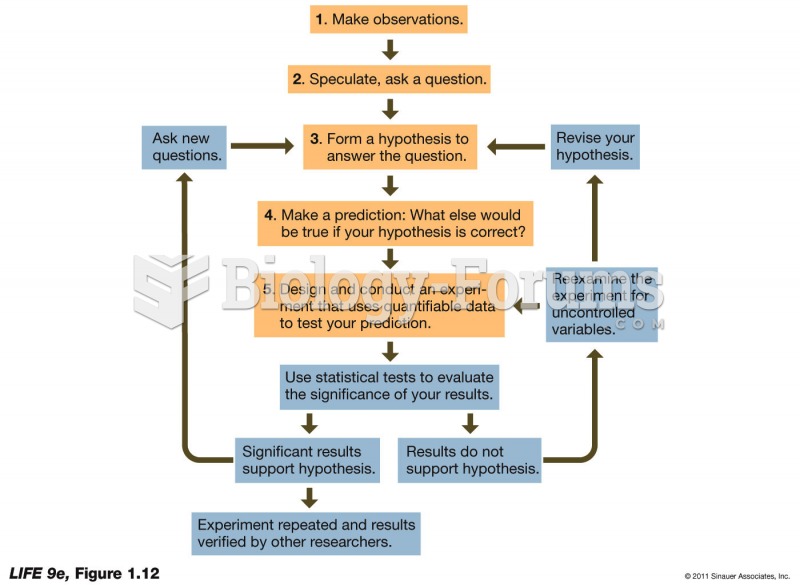
|
|
|
Despite claims by manufacturers, the supplement known as Ginkgo biloba was shown in a study of more than 3,000 participants to be ineffective in reducing development of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in older people.
Drugs are in development that may cure asthma and hay fever once and for all. They target leukotrienes, which are known to cause tightening of the air passages in the lungs and increase mucus productions in nasal passages.
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.
The average person is easily confused by the terms pharmaceutics and pharmacology, thinking they are one and the same. Whereas pharmaceutics is the science of preparing and dispensing drugs (otherwise known as the science of pharmacy), pharmacology is the study of medications.
The largest baby ever born weighed more than 23 pounds but died just 11 hours after his birth in 1879. The largest surviving baby was born in October 2009 in Sumatra, Indonesia, and weighed an astounding 19.2 pounds at birth.