|
|
|
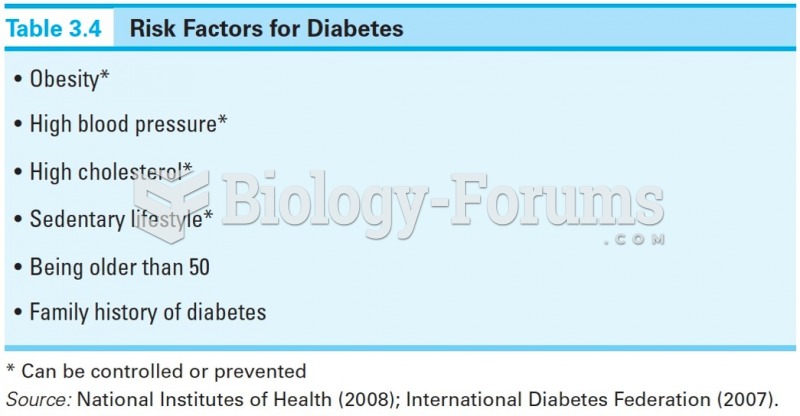
After 5 years of being diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, one every three patients will no longer be able to work.
The first monoclonal antibodies were made exclusively from mouse cells. Some are now fully human, which means they are likely to be safer and may be more effective than older monoclonal antibodies.
Eating food that has been cooked with poppy seeds may cause you to fail a drug screening test, because the seeds contain enough opiate alkaloids to register as a positive.
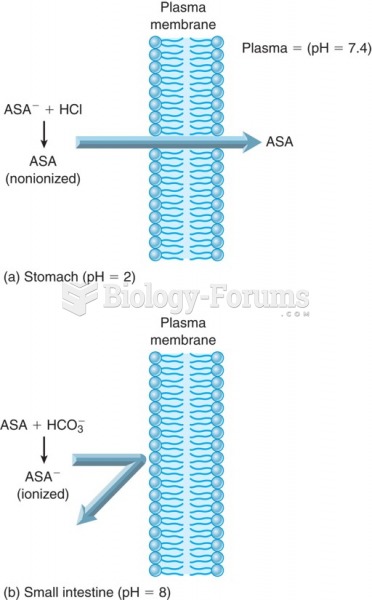
The use of salicylates dates back 2,500 years to Hippocrates's recommendation of willow bark (from which a salicylate is derived) as an aid to the pains of childbirth. However, overdosage of salicylates can harm body fluids, electrolytes, the CNS, the GI tract, the ears, the lungs, the blood, the liver, and the kidneys and cause coma or death.
Though Candida and Aspergillus species are the most common fungal pathogens causing invasive fungal disease in the immunocompromised, infections due to previously uncommon hyaline and dematiaceous filamentous fungi are occurring more often today. Rare fungal infections, once accurately diagnosed, may require surgical debridement, immunotherapy, and newer antifungals used singly or in combination with older antifungals, on a case-by-case basis.