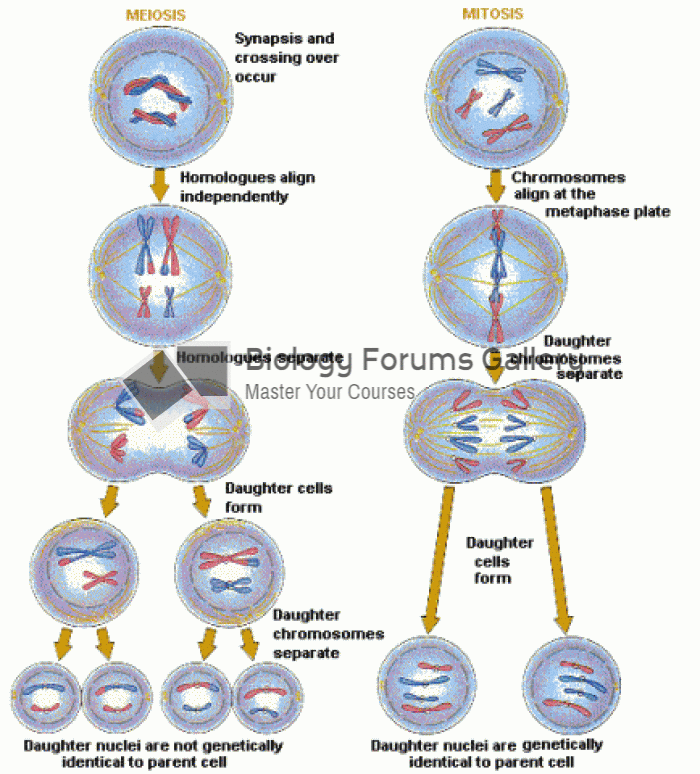
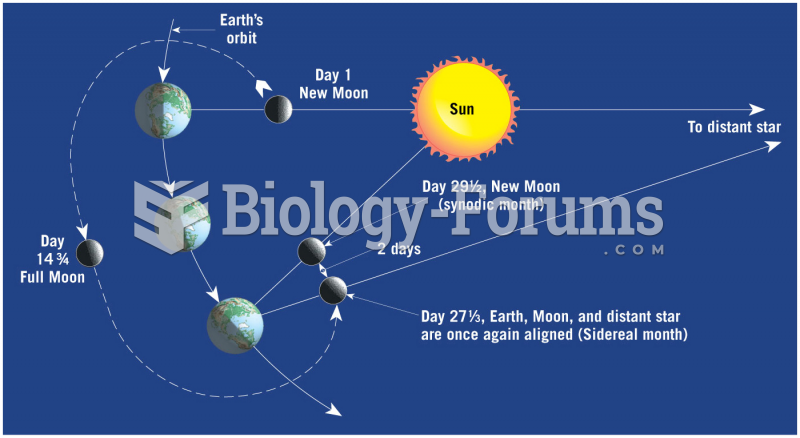
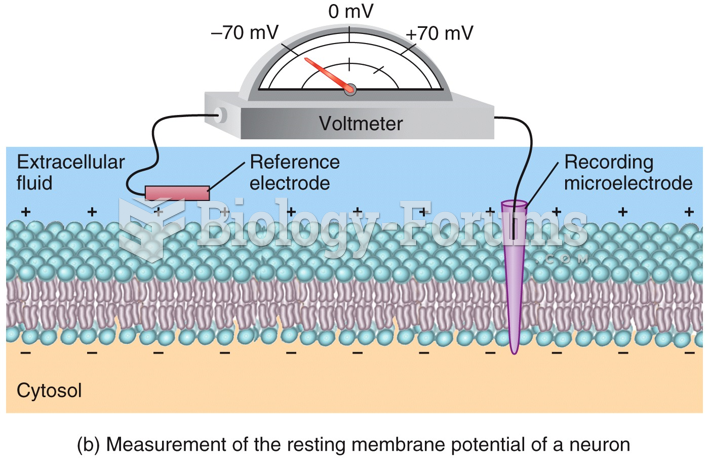
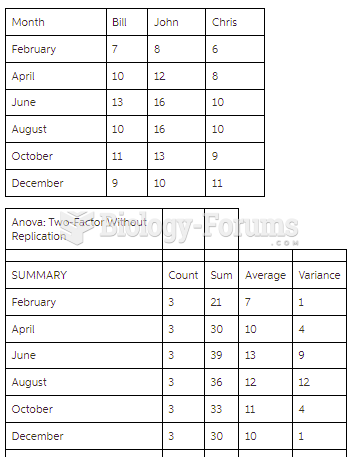
|
|
|
Asthma attacks and symptoms usually get started by specific triggers (such as viruses, allergies, gases, and air particles). You should talk to your doctor about these triggers and find ways to avoid or get rid of them.
The word drug comes from the Dutch word droog (meaning "dry"). For centuries, most drugs came from dried plants, hence the name.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis syndrome are life-threatening reactions that can result in death. Complications include permanent blindness, dry-eye syndrome, lung damage, photophobia, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, permanent loss of nail beds, scarring of mucous membranes, arthritis, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Many patients' pores scar shut, causing them to retain heat.
In 2012, nearly 24 milliion Americans, aged 12 and older, had abused an illicit drug, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.