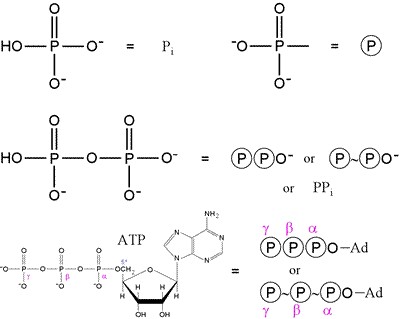
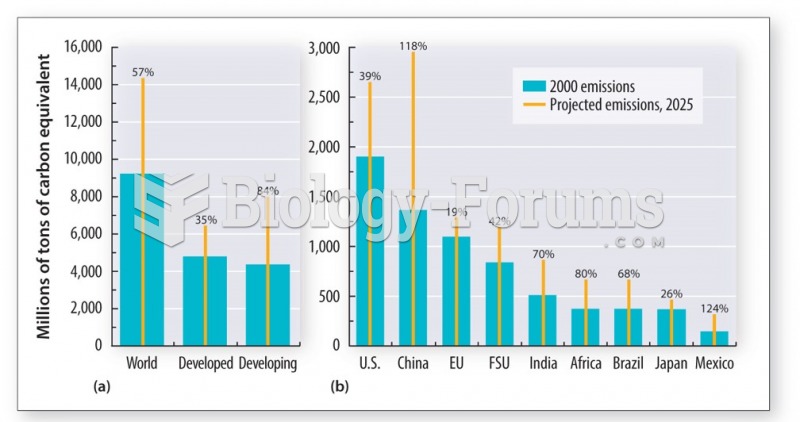
|
|
|
About 100 new prescription or over-the-counter drugs come into the U.S. market every year.
The newest statin drug, rosuvastatin, has been called a superstatin because it appears to reduce LDL cholesterol to a greater degree than the other approved statin drugs.
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis syndrome are life-threatening reactions that can result in death. Complications include permanent blindness, dry-eye syndrome, lung damage, photophobia, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, permanent loss of nail beds, scarring of mucous membranes, arthritis, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Many patients' pores scar shut, causing them to retain heat.
Every flu season is different, and even healthy people can get extremely sick from the flu, as well as spread it to others. The flu season can begin as early as October and last as late as May. Every person over six months of age should get an annual flu vaccine. The vaccine cannot cause you to get influenza, but in some seasons, may not be completely able to prevent you from acquiring influenza due to changes in causative viruses. The viruses in the flu shot are killed—there is no way they can give you the flu. Minor side effects include soreness, redness, or swelling where the shot was given. It is possible to develop a slight fever, and body aches, but these are simply signs that the body is responding to the vaccine and making itself ready to fight off the influenza virus should you come in contact with it.