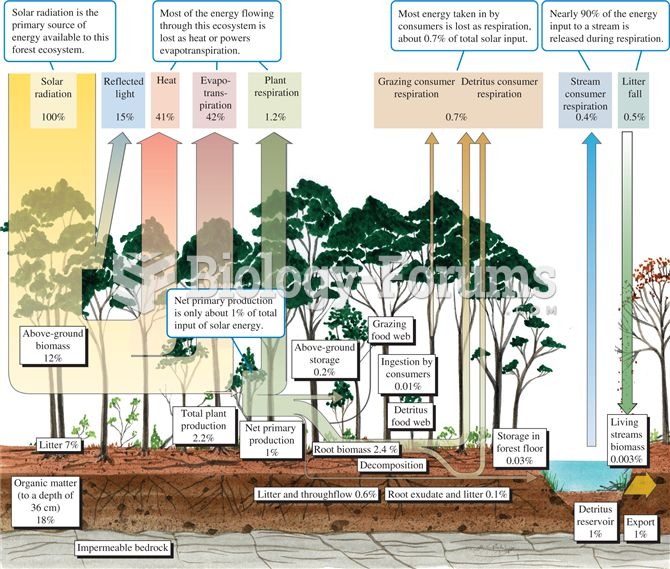
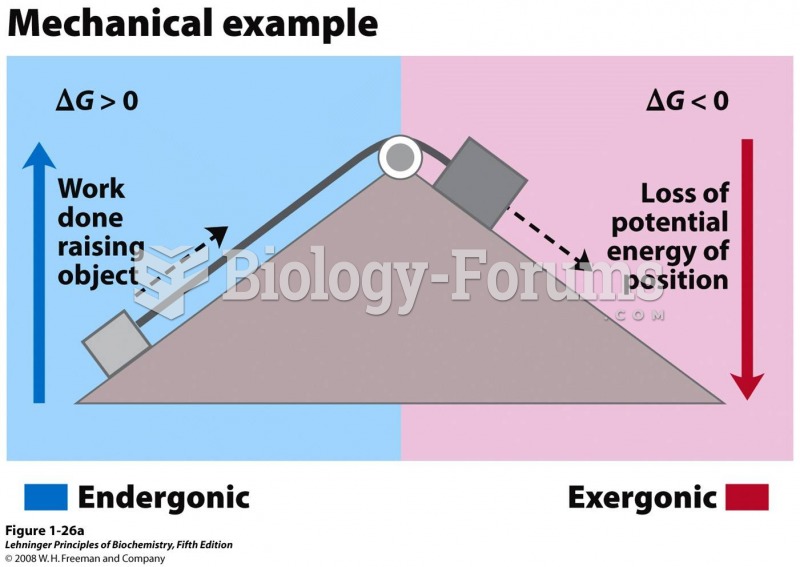
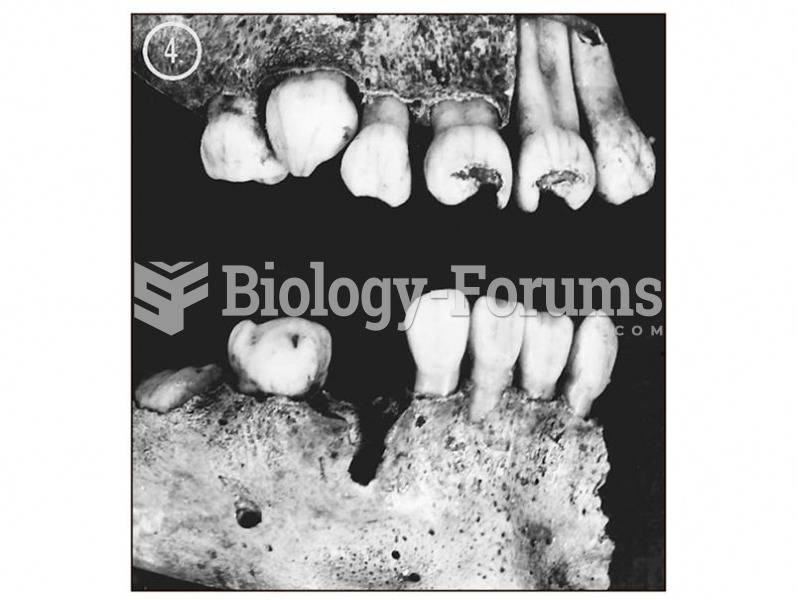
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
There are approximately 3 million unintended pregnancies in the United States each year.
Did you know?
After a vasectomy, it takes about 12 ejaculations to clear out sperm that were already beyond the blocked area.
Did you know?
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
Did you know?
Medications that are definitely not safe to take when breastfeeding include radioactive drugs, antimetabolites, some cancer (chemotherapy) agents, bromocriptine, ergotamine, methotrexate, and cyclosporine.