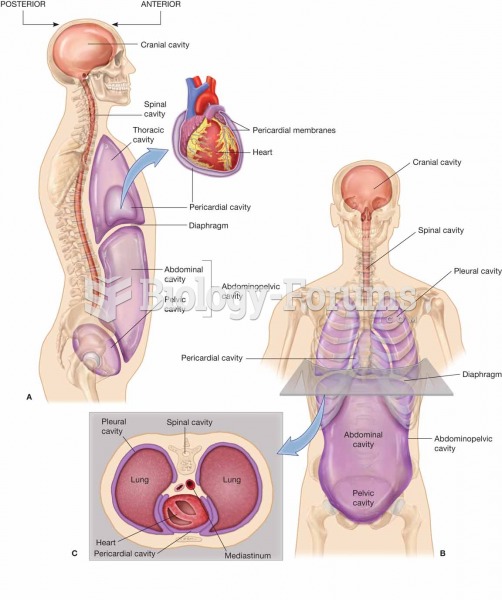
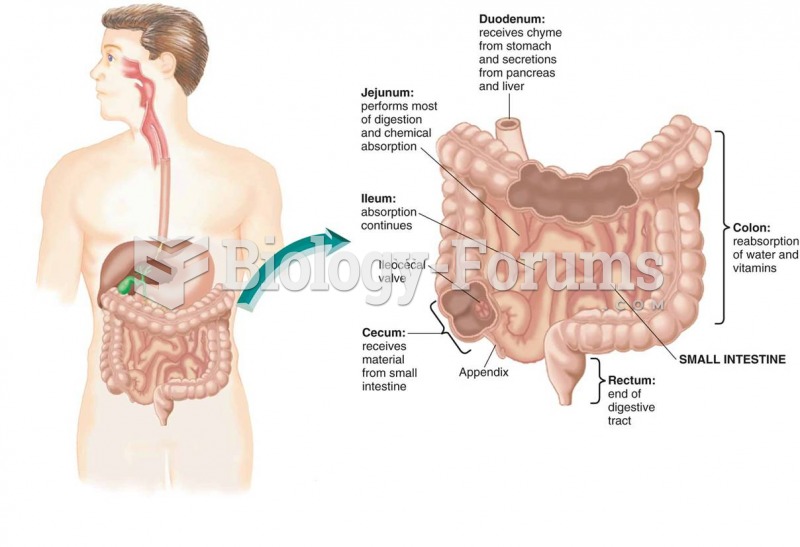
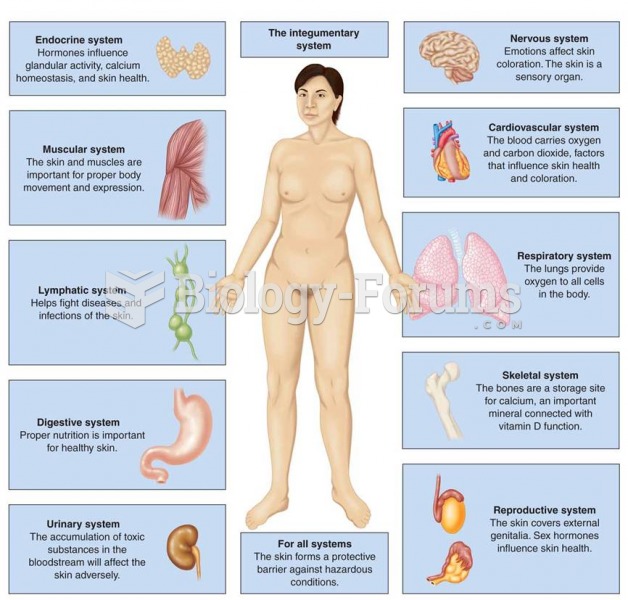
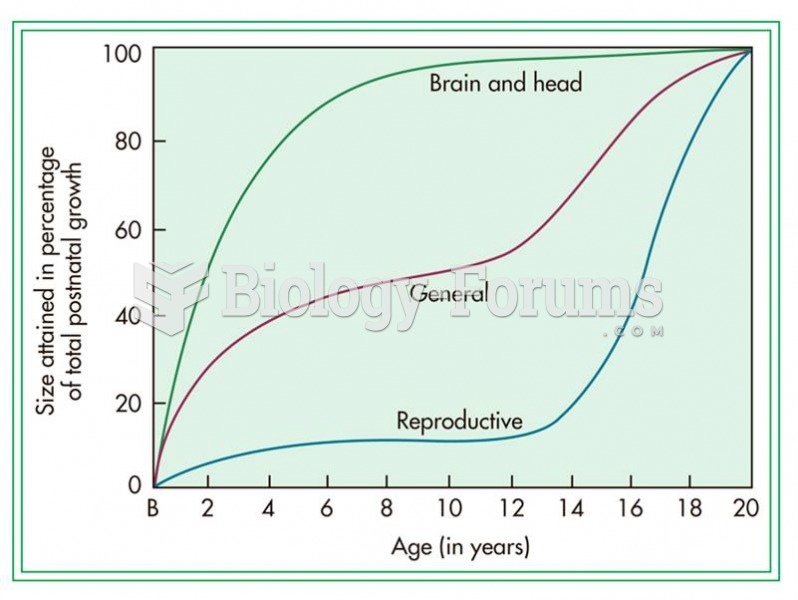
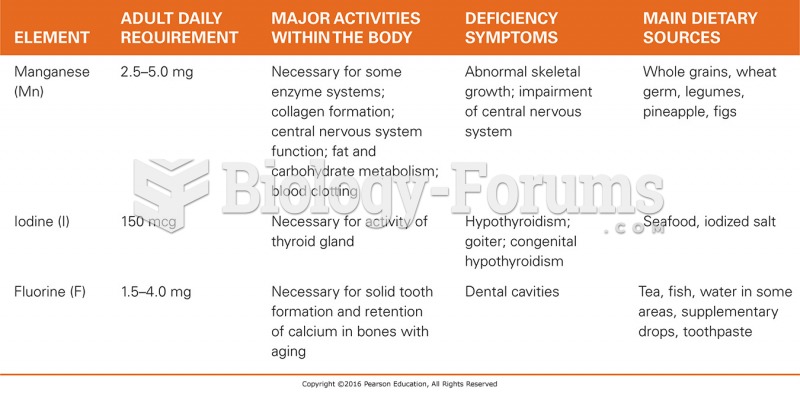
|
|
|
Drug-induced pharmacodynamic effects manifested in older adults include drug-induced renal toxicity, which can be a major factor when these adults are experiencing other kidney problems.
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
There are more bacteria in your mouth than there are people in the world.
Giardia is one of the most common intestinal parasites worldwide, and infects up to 20% of the world population, mostly in poorer countries with inadequate sanitation. Infections are most common in children, though chronic Giardia is more common in adults.
A good example of polar molecules can be understood when trying to make a cake. If water and oil are required, they will not mix together. If you put them into a measuring cup, the oil will rise to the top while the water remains on the bottom.