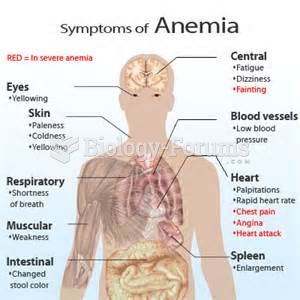
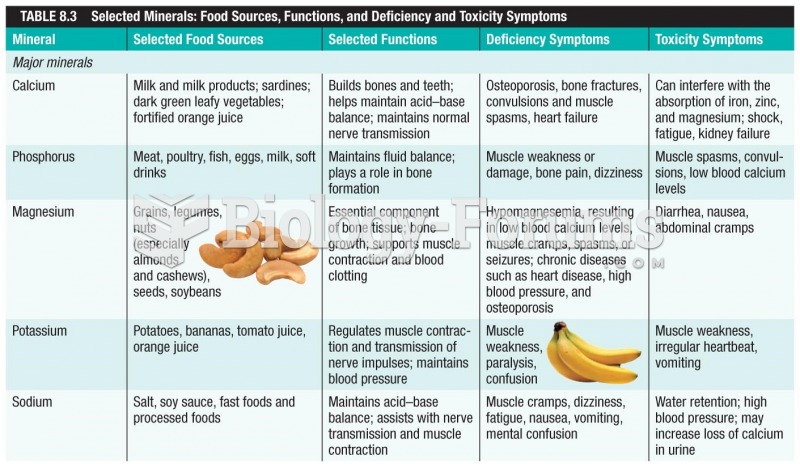
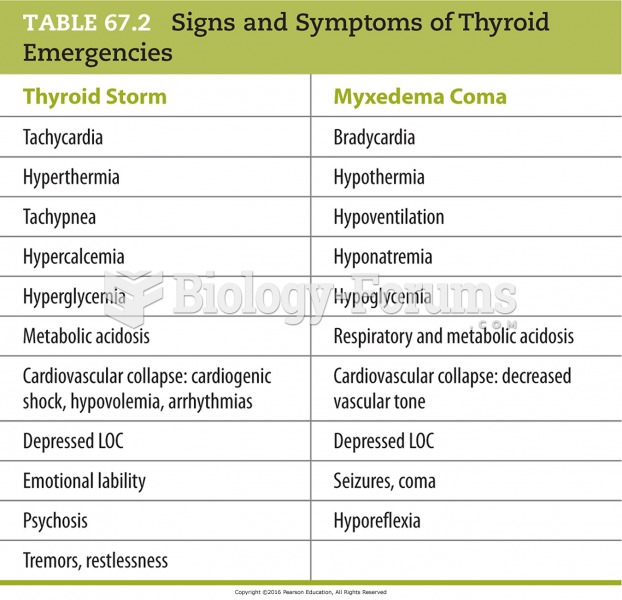
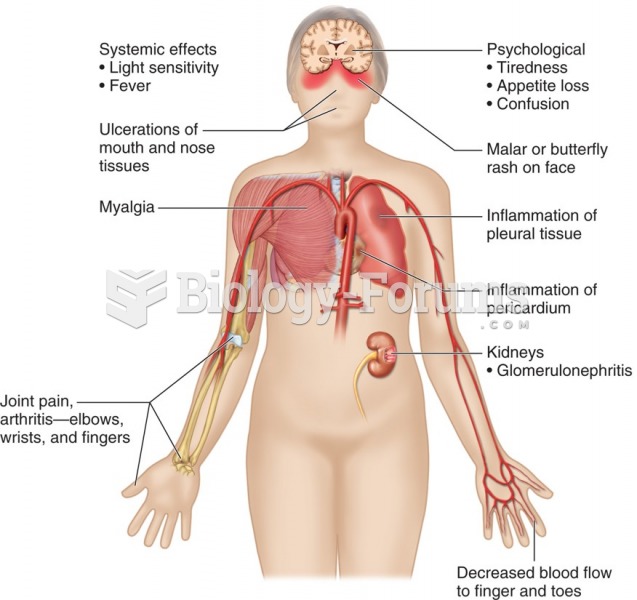
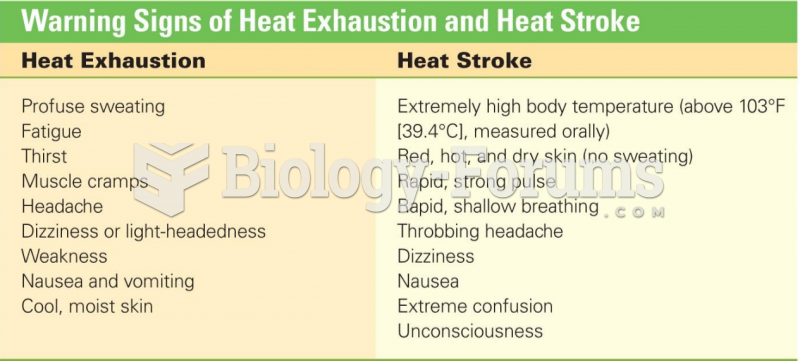
Answer to Question 1
Severe zinc deficiency is not widespread in developed countries, but in the developing world, nearly 2 billion people are zinc deficient. Human zinc deficiency was first reported in the 1960s in children and adolescent boys in Egypt, Iran, and Turkey. Children have especially high zinc needs because they are growing rapidly and synthesizing many zinc-containing proteins, and the native diets among those populations were not meeting these needs. Middle Eastern diets are traditionally low in the richest zinc source, meats. Furthermore, the staple foods in these diets are legumes, unleavened breads, and other whole-grain foodsall high in fiber and phytates, which inhibit zinc absorption.
Severe growth retardation and immature sexual development are characteristic of zinc deficiency. In addition, zinc deficiency hinders digestion and absorption, causing diarrhea, which worsens malnutrition not only for zinc, but for other nutrients as well. It also impairs the immune response, making infections likelyamong them, pneumonia and GI tract infections, which worsen malnutrition, including zinc malnutrition (a classic downward spiral of events). Chronic zinc deficiency damages the central nervous system and brain and may lead to poor motor development and cognitive performance. Because zinc deficiency directly impairs vitamin A metabolism, vitamin Adeficiency symptoms often appear. Zinc deficiency also disturbs thyroid function and the metabolic rate. It alters taste, causes loss of appetite, and slows wound healingin fact, its symptoms are so pervasive that generalized malnutrition and sickness are more likely to be the diagnosis than simple zinc deficiency.
Answer to Question 2
The hypothalamus regulates thyroid hormone production by controlling the release of the pituitary's thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). With iodine deficiency, thyroid hormone production declines, and the body responds by secreting more TSH in a futile attempt to accelerate iodide uptake by the thyroid gland. If a deficiency persists, the cells of the thyroid gland enlarge to trap as much iodide as possible. Sometimes the gland enlarges until it makes a visible lump in the neck, a goiter.
Goiter may be the earliest and most obvious sign of iodine deficiency, but the most tragic and prevalent damage occurs in the brain. Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of preventable mental retardation and brain damage in the world. Nearly one-third of the world's school-age children have iodine deficiency. Children with even a mild iodine deficiency typically have goiters and perform poorly in school. With sustained treatment, however, mental performance in the classroom as well as thyroid function improves.
Even in the United States, pregnant women may not get as much iodine as they need. A severe iodine deficiency during pregnancy causes the extreme and irreversible mental and physical retardation known as cretinism. Cretinism affects approximately 6 million people worldwide and can be averted by the early diagnosis and treatment of maternal iodine deficiency. A worldwide effort to provide iodized salt to people living in iodine-deficient areas has been dramatically successful. An estimated 70 percent of all households in developing countries have access to iodized salt. Because iron deficiency is common among people with iodine deficiency and because iron deficiency reduces the effectiveness of iodized salt, dual fortification with both iron and iodine may be most beneficial.
Excessive intakes of iodine can interfere with thyroid function and enlarge the gland, just as deficiency can. During pregnancy, exposure to excessive iodine from foods, prenatal supplements, or medications is especially damaging to the developing infant. An infant exposed to toxic amounts of iodine during gestation may develop a goiter so severe as to block the airways and cause suffocation. The UL is 1100 micrograms per day for an adultseveral times higher than average or recommended intakes.