|
|
|
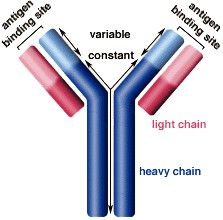
IgA antibodies protect body surfaces exposed to outside foreign substances. IgG antibodies are found in all body fluids. IgM antibodies are the first type of antibody made in response to an infection. IgE antibody levels are often high in people with allergies. IgD antibodies are found in tissues lining the abdomen and chest.
People with alcoholism are at a much greater risk of malnutrition than are other people and usually exhibit low levels of most vitamins (especially folic acid). This is because alcohol often takes the place of 50% of their daily intake of calories, with little nutritional value contained in it.
According to the CDC, approximately 31.7% of the U.S. population has high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad cholesterol" levels.
Street names for barbiturates include reds, red devils, yellow jackets, blue heavens, Christmas trees, and rainbows. They are commonly referred to as downers.
Approximately 15–25% of recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, many miscarriages often occur before a woman even knows she is pregnant.