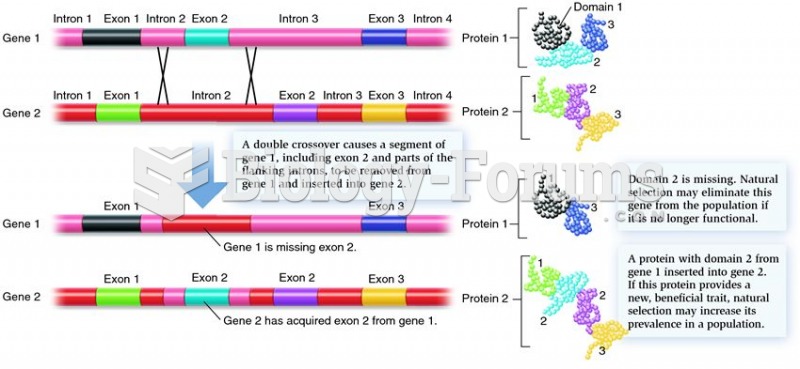
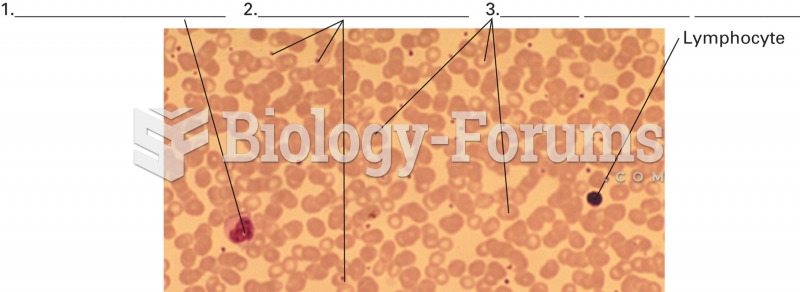
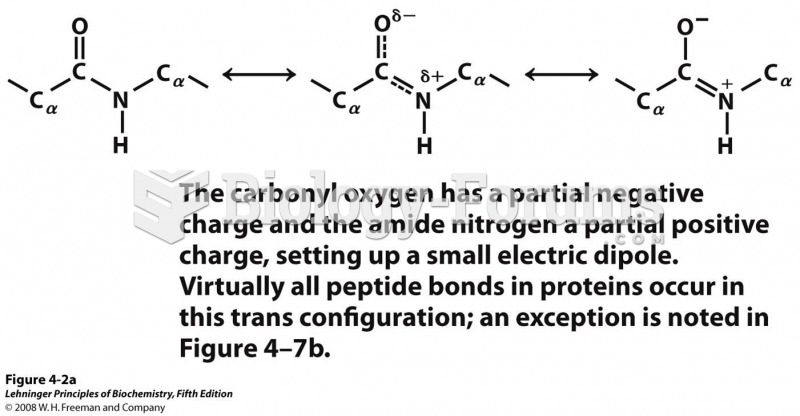
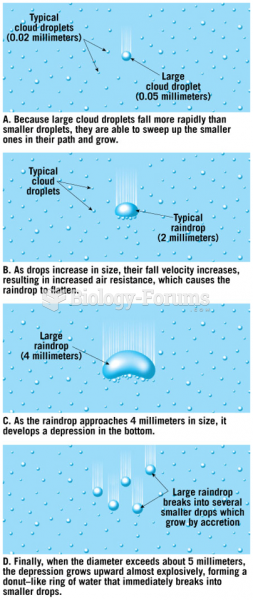
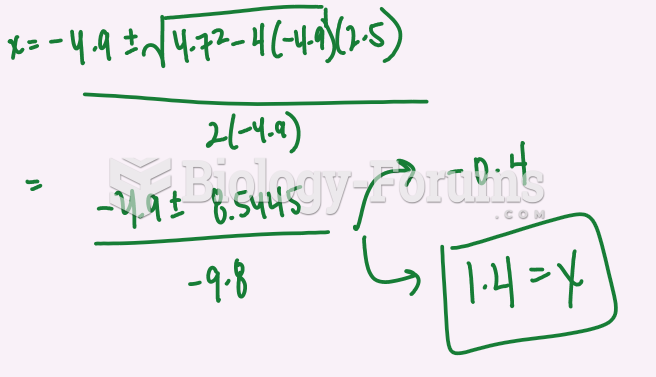Answer to Question 1
1) Step 1: Establish an open, warm environment and productive leaderparticipant relationships. Facilitators need to show empathy, appear warm and genuine, and use relationship-building responses, attentive behavior, and effective body language. Counselors should radiate positive energy indicating that you are looking forward to your time with the group members. The counselor is a model of trusting behavior for all group members to emulate to promote openness and interpersonal communication. Counselors may wish to start each meeting with an expression of intent to create an environment conducive to acceptance and open expression.
2) Step 2: Balance facilitator-generated and group- generated information. The challenge for nutrition counselors is to cover a preset curriculum and integrate client needs and experiences and allow the group to generate solutions and problem solve. Often counselors have a list of tasks identified as essential for clients to understand, but the facilitator-generated information will fall on deaf ears if group members have other concerns on their minds. One way to handle this potential problem is to ask participants in the first session to identify their pressing concerns. Then cover the most pressing problems first.
3) Step 3: Design problem-solving strategies. Many opportunities for group problem solving should be provided rather than having the counselor tell participants what they need to do. Social disclosure is a powerful force for behavior change. Group counseling provides an ideal setting for coupling group problem solving with this process. Participants design goals with feedback from the group and disclose their intent to accomplish certain tasks before the next group session.
4) Step 4: Provide the opportunity for group members to practice new skills. In step 3, the group worked as a whole to problem-solve or develop new strategies. Opportunities for each member to rehearse the skill can occur if members are divided into groups of two or three.
5) Step 5: Use positive role models and pacing to keep the group motivated. Spending time reviewing and understanding the successes of group members can provide a model for other participants to make alterations in their lifestyle. Successful members inspire others to follow their example and stay in the group. However, clients who are having difficulty and appear to be monopolizing the group time with their problems can be frustrating for the rest of the group. If counterproductive behaviors emerge, the counselor needs to block them from disrupting the group process. If necessary, the counselor should tell the client to stay after the session to receive personal attention.
6) Step 6: Ask for evaluation and feedback. Throughout the counseling process and after trying out a new activity or strategy, the facilitator should elicit feedback from the group. For example, Since we began meeting, what did you find particularly useful? or Did you find analyzing glucose records of previous clients useful?
Answer to Question 2
d