|
|
|
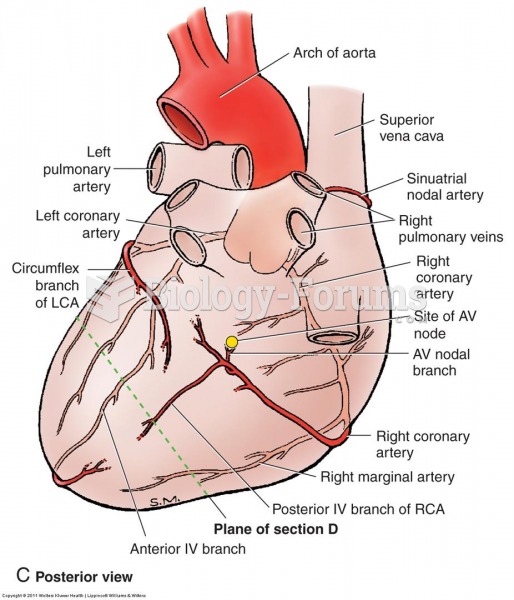
It is widely believed that giving a daily oral dose of aspirin to heart attack patients improves their chances of survival because the aspirin blocks the formation of new blood clots.
Russia has the highest death rate from cardiovascular disease followed by the Ukraine, Romania, Hungary, and Poland.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released reports detailing the deaths of infants (younger than 1 year of age) who died after being given cold and cough medications. This underscores the importance of educating parents that children younger than 2 years of age should never be given over-the-counter cold and cough medications without consulting their physicians.
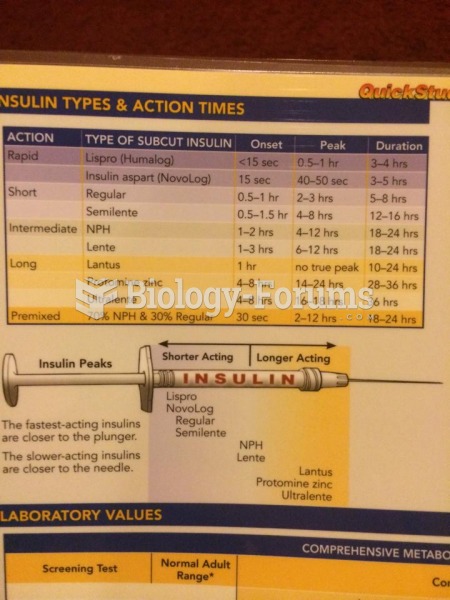
Many medications that are used to treat infertility are injected subcutaneously. This is easy to do using the anterior abdomen as the site of injection but avoiding the area directly around the belly button.
In ancient Rome, many of the richer people in the population had lead-induced gout. The reason for this is unclear. Lead poisoning has also been linked to madness.