|
|
|
Before a vaccine is licensed in the USA, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reviews it for safety and effectiveness. The CDC then reviews all studies again, as well as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Family Physicians. Every lot of vaccine is tested before administration to the public, and the FDA regularly inspects vaccine manufacturers' facilities.
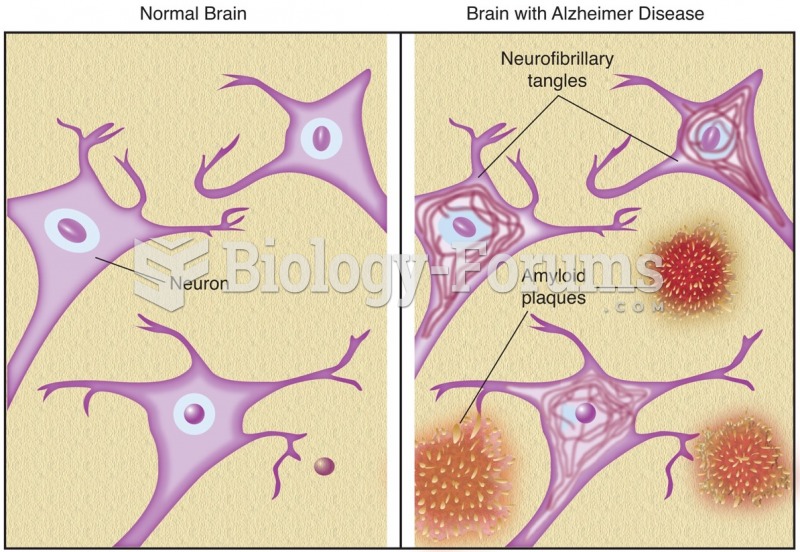
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system destroys its own healthy tissues. When this occurs, white blood cells cannot distinguish between pathogens and normal cells.
This year, an estimated 1.4 million Americans will have a new or recurrent heart attack.
The shortest mature adult human of whom there is independent evidence was Gul Mohammed in India. In 1990, he was measured in New Delhi and stood 22.5 inches tall.
Asthma occurs in one in 11 children and in one in 12 adults. African Americans and Latinos have a higher risk for developing asthma than other groups.