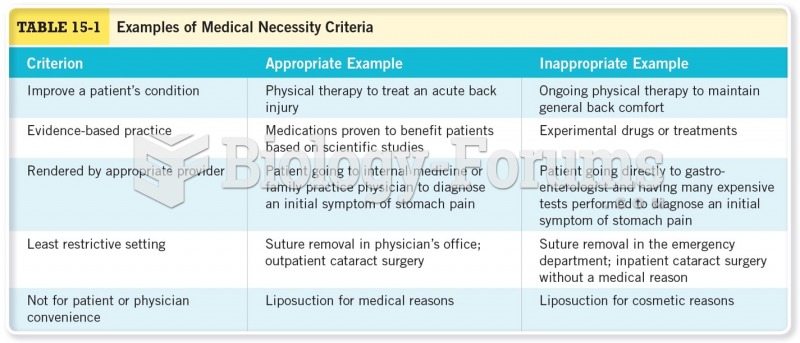
Answer to Question 1
According to the American Diabetes Association, T2DM is diagnosed using the following criteria:
- Fasting blood glucose levels 126 mg/dL
- Symptoms of diabetes plus casual blood glucose levels 200 mg/dL
Symptoms of polydipsia (excessive thirst), polyphagia (excessive hunger), and polyuria (frequent urination)
- Oral glucose tolerance test with a post-2 hr reading 200 mg/dL
HbA1c 6.5 is commonly used in practice as a confirmation of diabetes diagnosis
Mitch's record shows:
- Casual blood glucose level of 855 mg/dL (>200 mg/dL) at time of diagnosis
- HbA1c is 11.5 (significantly exceeds 6.5)
Answer to Question 2
Glycemic index (GI) is a ranking of the effects of various carbohydrate-containing foods on blood glucose levels. Each food's GI is based on a comparison of the effects of 50 grams of carbohydrate from that food to the effects of 50 grams of glucose.
Foods with a higher glycemic index produce a higher peak in postprandial glucose levels and a greater overall blood glucose response during the first 2 hours after consumption than foods with a lower glycemic index.
- Low GI is < 55; Medium is 56-69; High is > 70
GI is influenced by food preparation, cooking, etc., which may be a limitation of its usefulness.
Eating high-GI foods raises blood glucose levels faster. Thus, diabetics may be advised to consume lower-GI foods to help with glycemic control.
Foods high in protein, high in fat, or high in fiber tend to have a lower glycemic index.
GI can be misleading because the portion of each food tested must contain 50 g CHO. For example, carrots have a high glycemic index. However, it is unlikely that an individual would consume the portion size of carrots necessary to provide 50 g CHO ( 5.5 cups).
Glycemic load is calculated by multiplying the GI of foods / 100 by the net carbs in a portion of that food. Net carbs are the g of total carbs - the g of fiber.
- Glycemic load = GI / 100 x net carbs (total carbs - fiber). It is an attempt to quantify the overall glycemic effect of a portion of a food.
- Low is < 10; Medium is 11-19; High is > 20
When planning, eating foods with a lower GI may help control postprandial glucose values. These values also contribute to HbA1c values, ultimately helping with glycemic control.
It is important for the client to understand that not all low-GI foods are healthy choices and that not all foods have been tested to determine their glycemic index, making it a useful tool, but a tool that should be used in addition to other planning tools. The evidence supporting glycemic index and glycemic load for diabetics is conflicting.