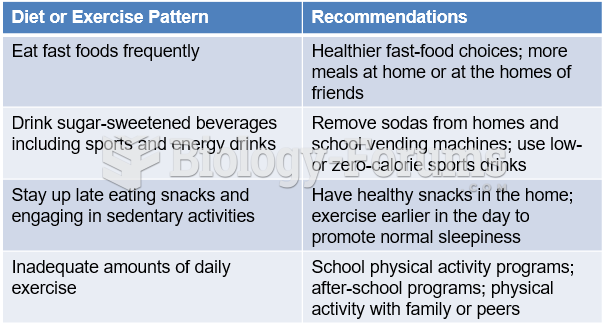
Answer to Question 1
The standard guidelines and subsequent recommendations for weaning TPN depend on when enteral feedings or PO intake has been advanced to >60 of estimated energy needs. Once this occurs and the patient is tolerating the alternate route of feeding well, the PN formula can be discontinued. Attention to glycemic control post-PN is important to monitor for hypoglycemia. If the patient has a history of hypoglycemia, however, it is reasonable to taper PN over 1-2 hours to avoid this problem. Overall, it is important to meet calorie needs through the transition of PN to EN for this patient in order to avoid complications with glycemic control or underfeeding.
Answer to Question 2
UC and CD are very similar, but can be distinguished from one another by the following:
Symptoms
Complications
Antibody testing
Imaging and biopsy results
Crohn's disease Ulcerative colitis
Symptoms Blood &/or mucus in stool
Abdominal pain & cramping
Fever
Wt loss
Chronic diarrhea
Anorexia
Malnutrition
Delayed growth in adolescents Bloody diarrhea with mucus
Abdominal &/or rectal pain
Fever
Wt loss
Possibly constipation & rectal spasm
Arthritis
Dermatological changes
Ocular manifestations
Complications Malabsorption
Malnutrition
Abdominal fistulas & abscesses
Intestinal obstruction
Bacterial overgrowth (blind loop syndrome)
Gallstones
Perianal disease
Neoplasia
Urinary tract infections
Kidney stones
Thromboembolic complications
Affects any part of the GI tract (from mouth to anus) and may have a skipping pattern Severe bleeding
Toxic colitis
Toxic megacolon
Strictures
Perforation
Colonic structures
Dysplasia
Carcinoma
Intolerance to immunosuppression
Affects the colon and rectum only (continuous)
Diagnosis Clinical presentation CDAI score
Abdominal ultrasound
MRI
CT
Antiglycan antibodies (ASCA/ANCA)
Calprotectin, lactoferrin, & polymorphonuclear neutrophil elastase Abdominal ultrasound
MRI
CT
Antiglycan antibodies (ASCA/ANCA)
Calprotectin, lactoferrin, & polymorphonuclear neutrophil elastase