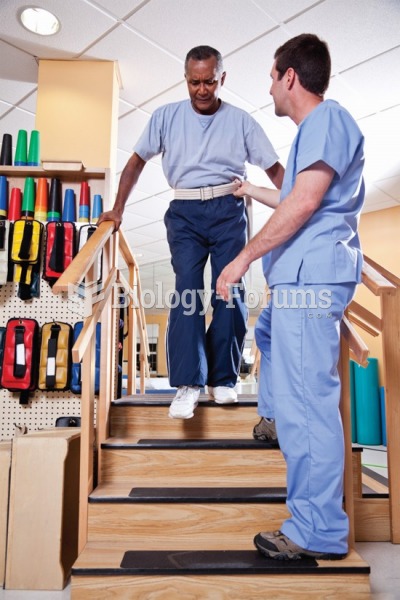
Answer to Question 1 Dysphagia refers to difficulty swallowing; it can be a medical or feeding issue at any age and is more prevalent in older adults.
Muscle weakness, incoordination, impaired gag or swallow reflexes, and impaired cough contribute to dysphagia; it may result from neurological disorders, degenerative diseases, cancers, or postintubation traumas.
Complications that can be associated with dysphagia include inadequate oral intake, unintended weight loss leading to malnutrition, aspiration pneumonia, dehydration, depression, decreased rehabilitation potential, increased length of hospital stay, and increased medical costs. There are many nutritional concerns because the ability to eat by mouth efficiently and successfully is compromised by difficulties with chewing and swallowing.
Answer to Question 2 Since vitamin B6 is a cofactor for DOPA decarboxylase, an enzyme needed to convert L-dopa to dopamine, excessive B6 supplementation may cause a rapid conversion rate before the drug can reach the brain. Therefore, supplement levels greater than 15 mg are not recommended. Additionally, high protein meals can interfere with the efficacy of levadopa as amino acids compete for the carriers to transport them across the blood-brain barrier.
Sinemet: carbidopa/levodopa, 50/200 mg controlled-release tablet twice daily
This combination reduces the effective dose of levodopa. Carbidopa is also a levodopa enhancer and helps reduce the side effects of nausea and vomiting.
Patients taking Sinemet may experience side effects including dyskinesia, or involuntary and erratic movements of the face, arms, legs, or trunk of body (this can occur 1-2 hours after taking Sinemet when it is at its peak clinical effect); N/V; loss of appetite; constipation; diarrhea; dryness of moth; flatulence; abdominal pain; lowered BP; and confusion.
Citalopram 20 mg daily
Used to treat depression; in a class of antidepressants called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors that are thought to work by increasing the amount of serotonin
This medication may cause N/V, constipation, diarrhea, stomach pain, heartburn, weight loss, decreased appetite, excessive tiredness, muscle or joint pain, and dry mouth
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001041/ Esomeprazole 20 mg daily
Used to treat the symptoms of GERD and to decrease the risk for developing stomach ulcers
May cause headache, dry mouth, constipation; more severe symptoms include difficulty breathing or swallowing, itching, dizziness, hoarseness, and excessive tiredness
No drug-nutrient interactions
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001062/ Omega-3-fatty acids 1000 mg daily
Omega fatty acids may be neuroprotective with a progressive neurological disorder; like ketogenic diets, these fatty acids are thought to improve symptoms, but more research is needed in this area
No drug-nutrient interactions