|
|
|
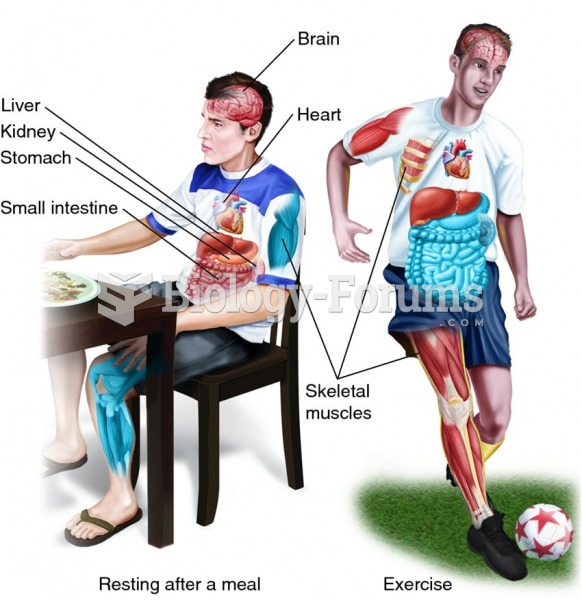
Human kidneys will clean about 1 million gallons of blood in an average lifetime.
Hip fractures are the most serious consequences of osteoporosis. The incidence of hip fractures increases with each decade among patients in their 60s to patients in their 90s for both women and men of all populations. Men and women older than 80 years of age show the highest incidence of hip fractures.
The immune system needs 9.5 hours of sleep in total darkness to recharge completely.
Every 10 seconds, a person in the United States goes to the emergency room complaining of head pain. About 1.2 million visits are for acute migraine attacks.
There are major differences in the metabolism of morphine and the illegal drug heroin. Morphine mostly produces its CNS effects through m-receptors, and at k- and d-receptors. Heroin has a slight affinity for opiate receptors. Most of its actions are due to metabolism to active metabolites (6-acetylmorphine, morphine, and morphine-6-glucuronide).