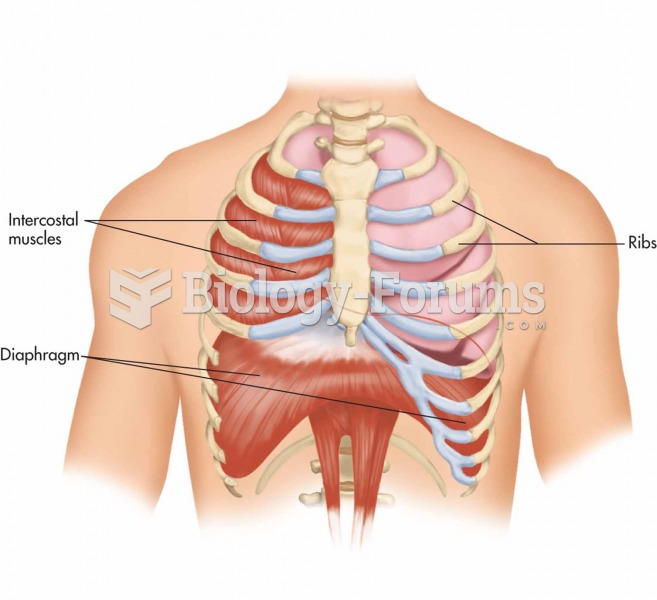
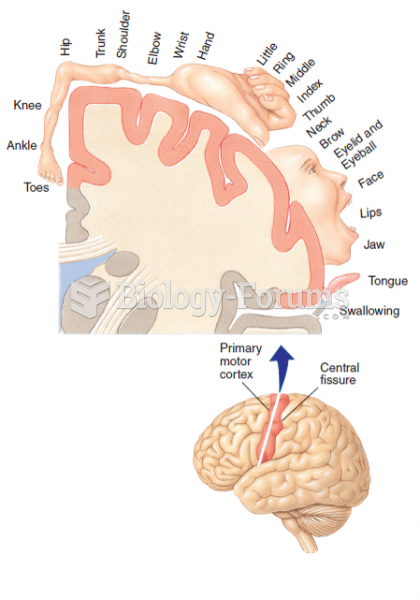
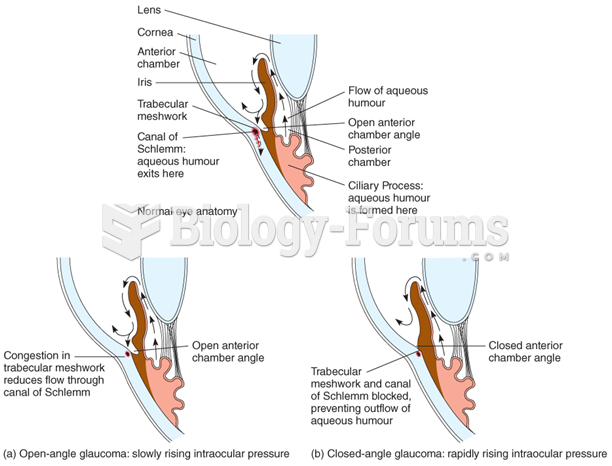
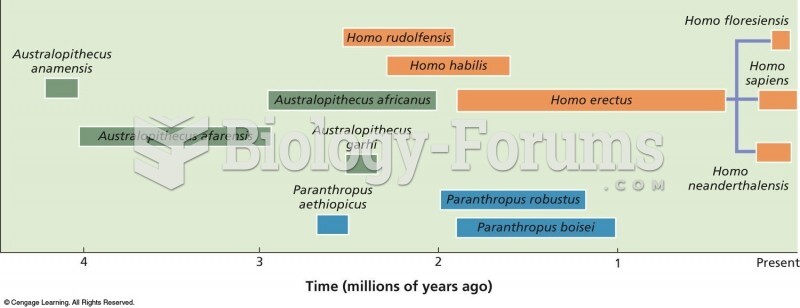
Answer to Question 1
Primary producers in the ocean include seed-bearing plants (anthophyta), various types of marine macro algae (the seaweeds) and micro-algae. The only members of kingdom Plantae that exist in the marine environment belong to the seed-bearing members of phylum Anthophyta (antho = flower, phytum = plant), which occur exclusively in shallow coastal areas. Eelgrass (Zosterais), a grasslike plant with true roots, exists primarily in the quiet waters of bays and estuaries from the low-tide zone to a depth of 6 meters. Various types of marine macro algae (the seaweeds) are typically found in shallow waters along the ocean margins. These algae are usually attached to the bottom, but a few species float. Algae are classified in part based on the color of the pigment they contain. Although modern classification of algae uses more than just its color, the division of algae into groups based on color is still a useful means of describing the different types of algae. Green Algae of phylum Chlorophyta are common in freshwater environments; they are not well represented in the ocean. Most marine species are intertidal or grow in shallow bay waters. Various species of sea lettuce (Ulva), a thin membranous sheet only two cell layers thick, are widely scattered throughout cold-water areas. Sponge weed (Codium), a two-branched form more common in warm waters, can exceed 6 meters in length. Red algae of phylum Rhodophyta are the most abundant and widespread of marine macroscopic algae. Over 4000 species occur from the very highest intertidal levels to the outer edge of the inner sublittoral zone. Brown algae of the phylum Phaeophyta include the largest members of the attached species of marine algae. Their color ranges from very light brown to black. Brown algae occur primarily in middle latitude, cold-water areas. The sizes of brown algae range widely. One of the smallest is Ralfsia, which occurs as a dark brown encrusting patch in upper and middle intertidal zones. One of the largest is bull kelp (Pelagophycus), which may grow in water deeper than 30 meters and extend to the surface. Other types of brown algae include Sargassum after which the Sargasso Sea is named and Macrocystis. Most microscopic algae are phytoplankton. The golden algae of phylum Chrysophyta contain the orange-yellow pigment carotin. They consist of diatoms and coccolithophores, both of which store food as carbohydrates and oils. Diatoms are a class of algae that are contained in a microscopic shell composed of opaline silica (SiO2 nH2O.) Coccolithophores are covered with small calcareous plates called coccoliths, made of calcium carbonate. Dinoflagellates belong to the phylum Pyrrophyta. They possess flagella for locomotion, giving them a slight capacity to move into areas that are more favorable for photosynthetic productivity. Dinoflagellate tests are made of cellulose.
Answer to Question 2
Eutrophic parts of the ocean have high chlorophyll concentrations meaning that they are highly productive areas. In general, eutrophic waters are naturally found in shallow-water coastal regions, areas of upwelling, and high-latitude regions. Areas of low chlorophyll concentration (low productivity) are called oligotrophic and are found in the open oceans of the tropics.