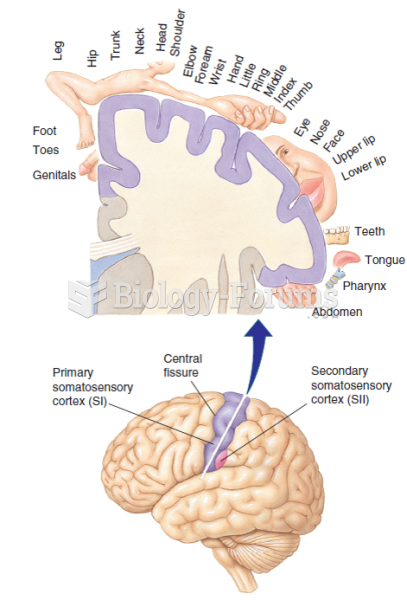
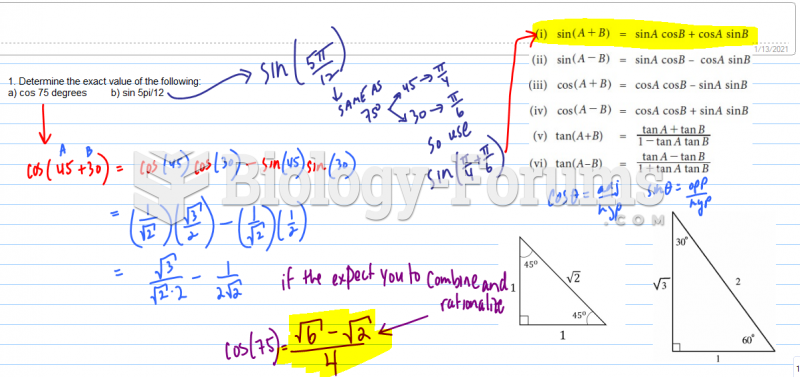
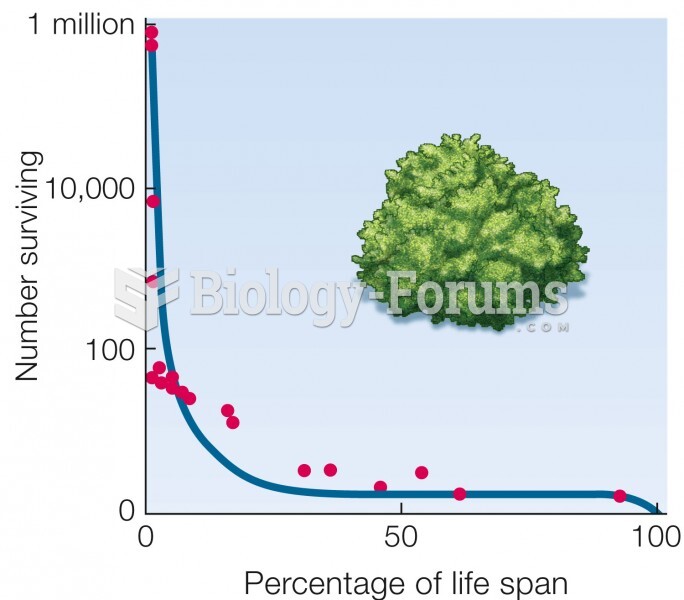
|
|
|
The most common childhood diseases include croup, chickenpox, ear infections, flu, pneumonia, ringworm, respiratory syncytial virus, scabies, head lice, and asthma.
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors, people should avoid a variety of foods, which include alcoholic beverages, bean curd, broad (fava) bean pods, cheese, fish, ginseng, protein extracts, meat, sauerkraut, shrimp paste, soups, and yeast.
The National Institutes of Health have supported research into acupuncture. This has shown that acupuncture significantly reduced pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee, when used as a complement to conventional therapies.
Signs and symptoms of a drug overdose include losing consciousness, fever or sweating, breathing problems, abnormal pulse, and changes in skin color.
A good example of polar molecules can be understood when trying to make a cake. If water and oil are required, they will not mix together. If you put them into a measuring cup, the oil will rise to the top while the water remains on the bottom.