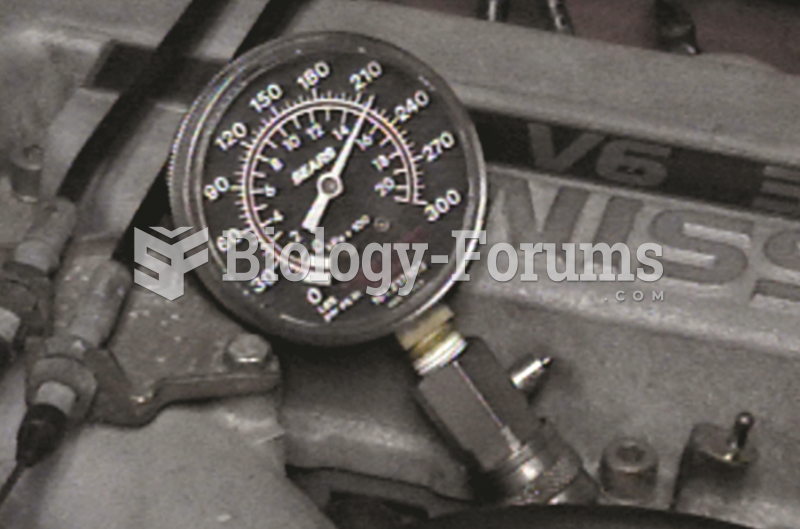
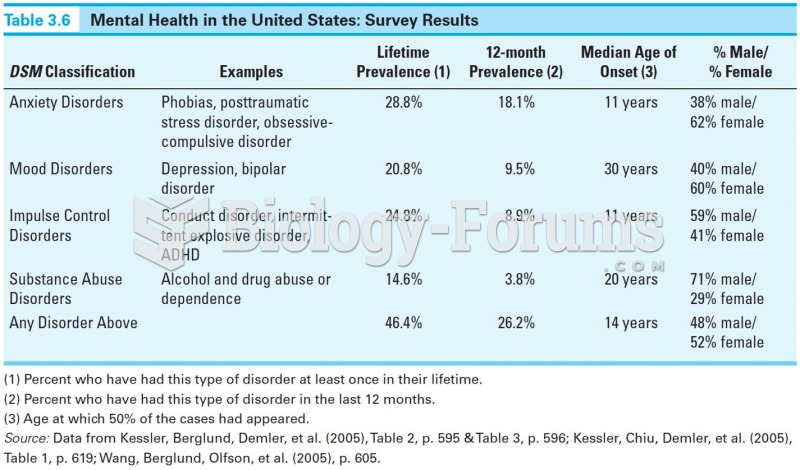
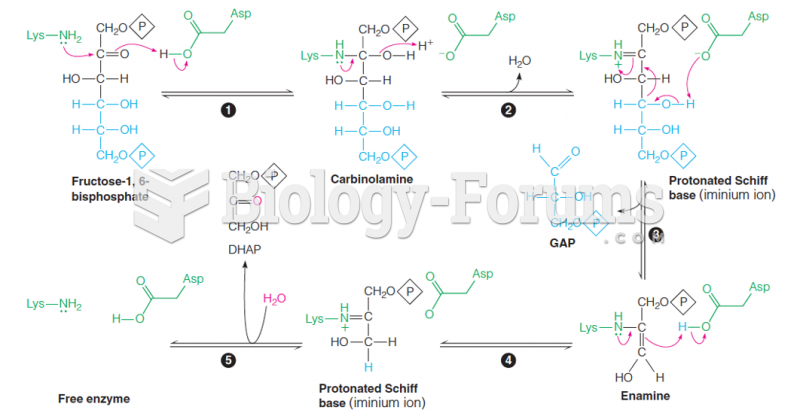
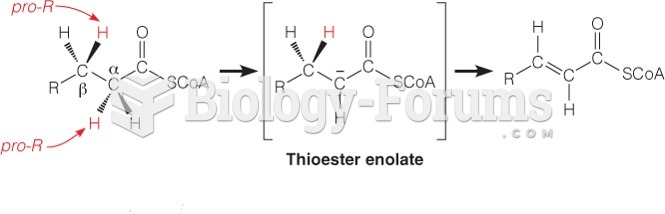
|
|
|
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
Asthma occurs in one in 11 children and in one in 12 adults. African Americans and Latinos have a higher risk for developing asthma than other groups.
Your chance of developing a kidney stone is 1 in 10. In recent years, approximately 3.7 million people in the United States were diagnosed with a kidney disease.
Since 1988, the CDC has reported a 99% reduction in bacterial meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae, due to the introduction of the vaccine against it.
People often find it difficult to accept the idea that bacteria can be beneficial and improve health. Lactic acid bacteria are good, and when eaten, these bacteria improve health and increase longevity. These bacteria included in foods such as yogurt.