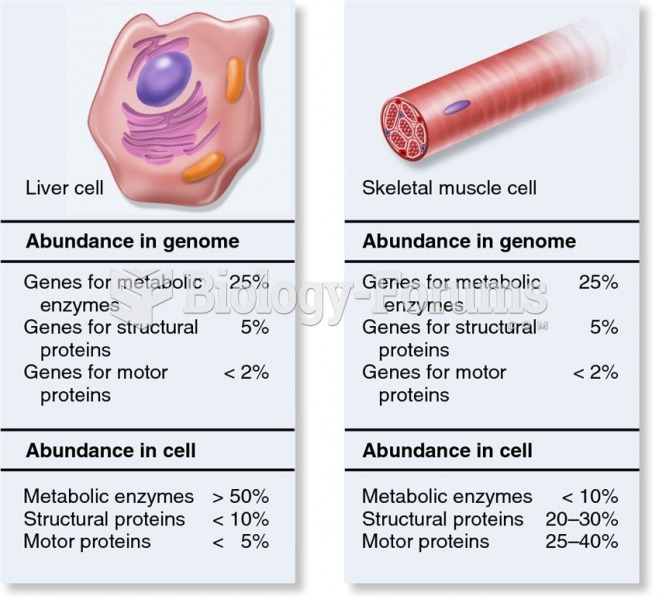
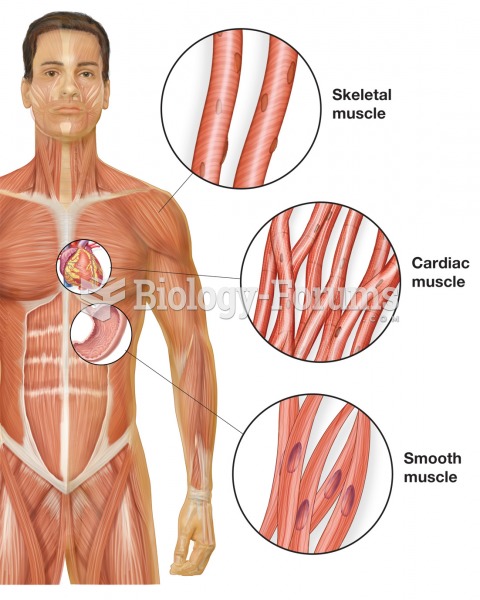
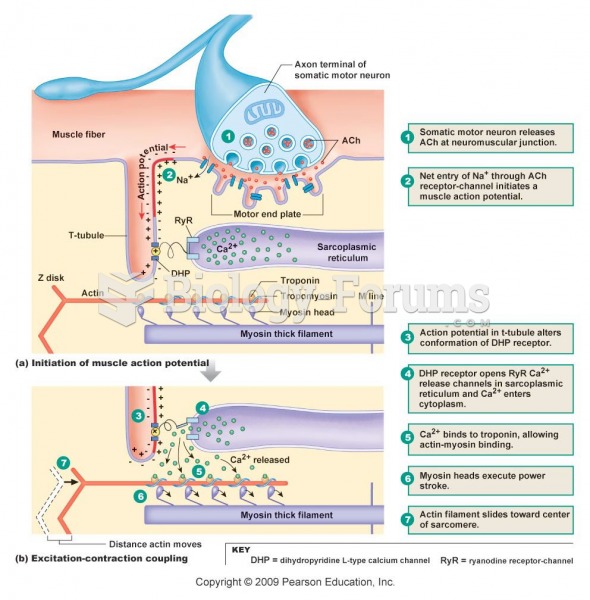
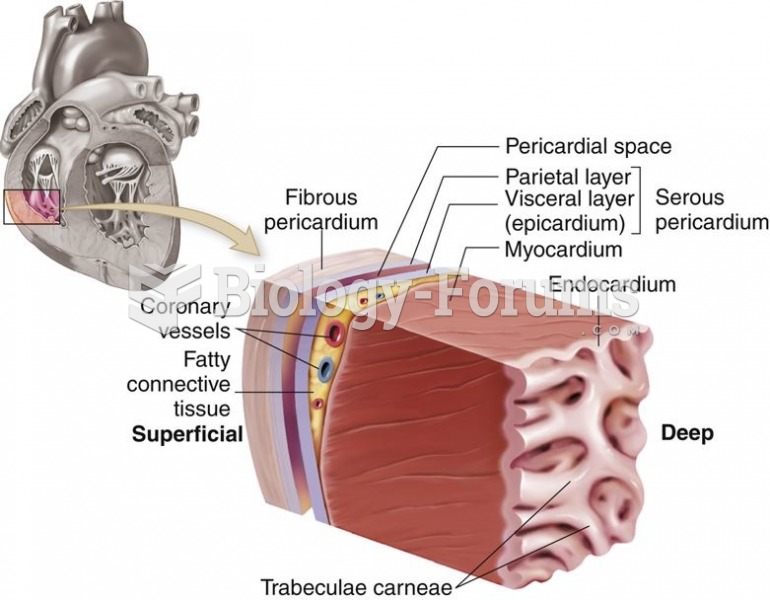
|
|
|
Drug-induced pharmacodynamic effects manifested in older adults include drug-induced renal toxicity, which can be a major factor when these adults are experiencing other kidney problems.
Drug abusers experience the following scenario: The pleasure given by their drug (or drugs) of choice is so strong that it is difficult to eradicate even after years of staying away from the substances involved. Certain triggers may cause a drug abuser to relapse. Research shows that long-term drug abuse results in significant changes in brain function that persist long after an individual stops using drugs. It is most important to realize that the same is true of not just illegal substances but alcohol and tobacco as well.
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.
Before a vaccine is licensed in the USA, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reviews it for safety and effectiveness. The CDC then reviews all studies again, as well as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Family Physicians. Every lot of vaccine is tested before administration to the public, and the FDA regularly inspects vaccine manufacturers' facilities.
According to research, pregnant women tend to eat more if carrying a baby boy. Male fetuses may secrete a chemical that stimulates their mothers to step up her energy intake.