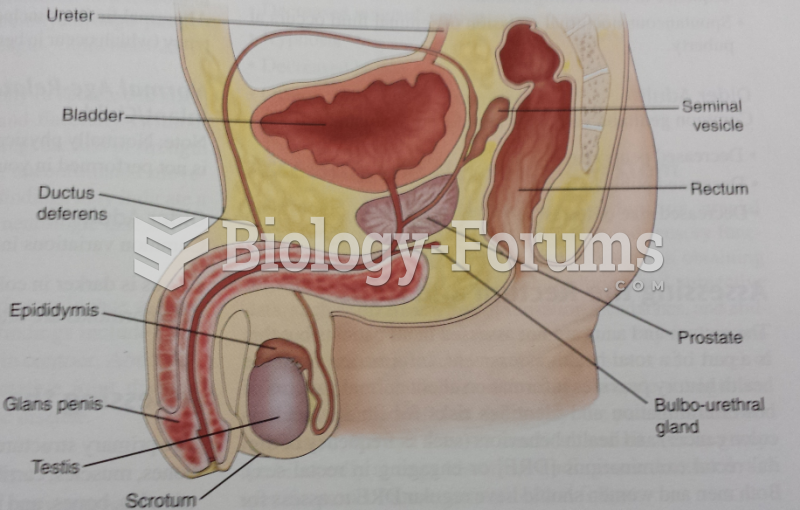
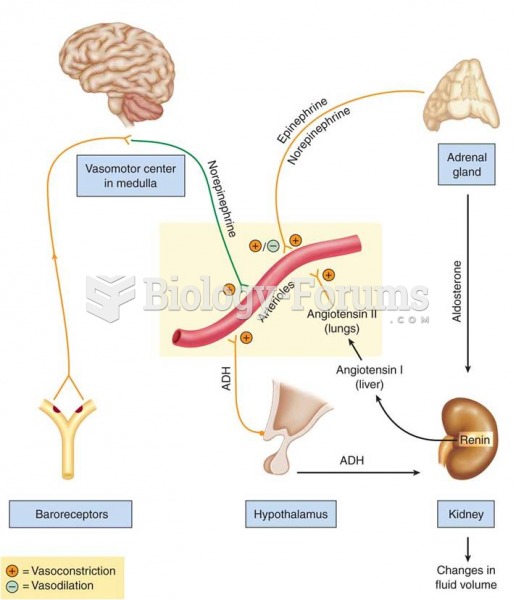
|
|
|
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
Disorders that may affect pharmacodynamics include genetic mutations, malnutrition, thyrotoxicosis, myasthenia gravis, Parkinson's disease, and certain forms of insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) was originally known as the Communicable Disease Center, which was formed to fight malaria. It was originally headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, since the Southern states faced the worst threat from malaria.
Famous people who died from poisoning or drug overdose include, Adolf Hitler, Socrates, Juan Ponce de Leon, Marilyn Monroe, Judy Garland, and John Belushi.
Fewer than 10% of babies are born on their exact due dates, 50% are born within 1 week of the due date, and 90% are born within 2 weeks of the date.