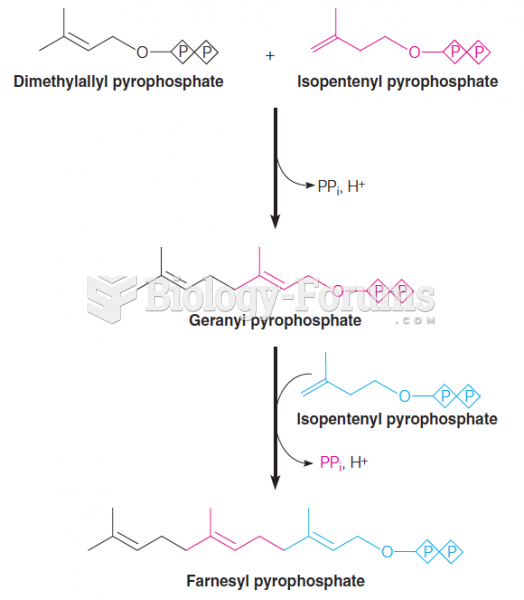
|
|
|
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.
Interferon was scarce and expensive until 1980, when the interferon gene was inserted into bacteria using recombinant DNA technology, allowing for mass cultivation and purification from bacterial cultures.
Most strokes are caused when blood clots move to a blood vessel in the brain and block blood flow to that area. Thrombolytic therapy can be used to dissolve the clot quickly. If given within 3 hours of the first stroke symptoms, this therapy can help limit stroke damage and disability.
Multiple experimental evidences have confirmed that at the molecular level, cancer is caused by lesions in cellular DNA.
Patients who have been on total parenteral nutrition for more than a few days may need to have foods gradually reintroduced to give the digestive tract time to start working again.