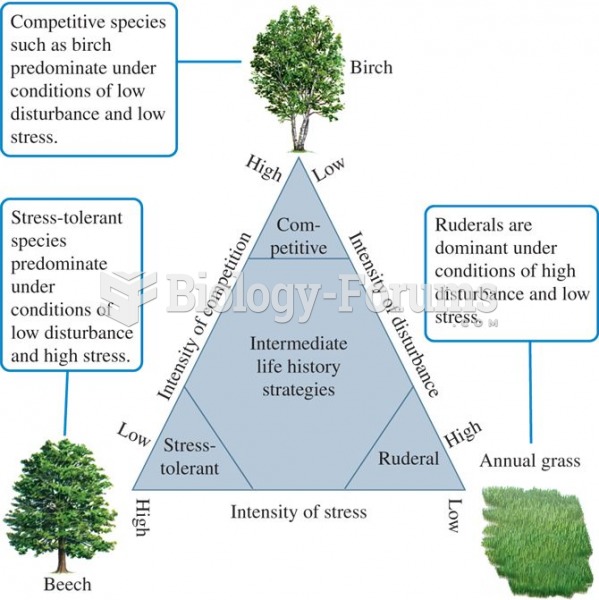
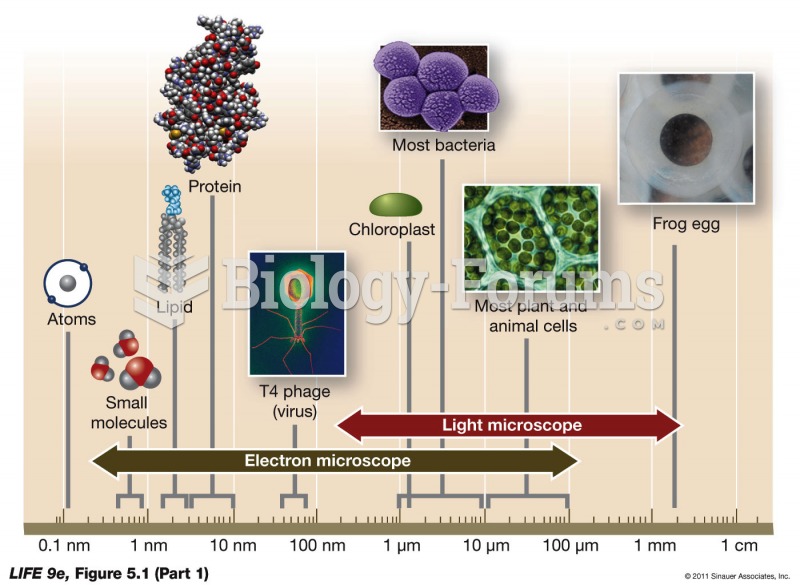
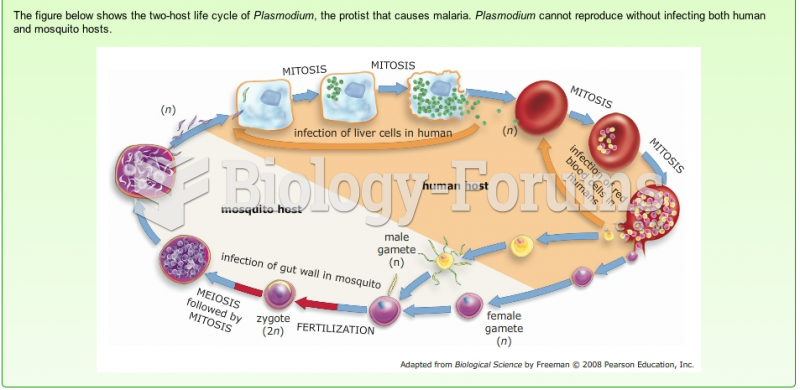
|
|
|
More than 30% of American adults, and about 12% of children utilize health care approaches that were developed outside of conventional medicine.
Malaria was not eliminated in the United States until 1951. The term eliminated means that no new cases arise in a country for 3 years.
Approximately one in three babies in the United States is now delivered by cesarean section. The number of cesarean sections in the United States has risen 46% since 1996.
Of the estimated 2 million heroin users in the United States, 600,000–800,000 are considered hardcore addicts. Heroin addiction is considered to be one of the hardest addictions to recover from.
After 5 years of being diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, one every three patients will no longer be able to work.